Cyber threats are growing fast — and getting smarter. For many companies, traditional security tools just can’t keep up with the sheer speed and complexity of modern attacks. That’s where Artificial Intelligence (AI) steps in. It doesn’t just add extra muscle — it completely changes the way we defend digital systems.
By spotting unusual patterns in massive data flows, AI helps detect threats in real time and takes care of routine responses automatically. This speeds up detection and eases the load on human teams. According to IBM, organizations using AI can reduce the time it takes to contain a breach by as much as 14 weeks — and save an average of $1.76 million per incident.
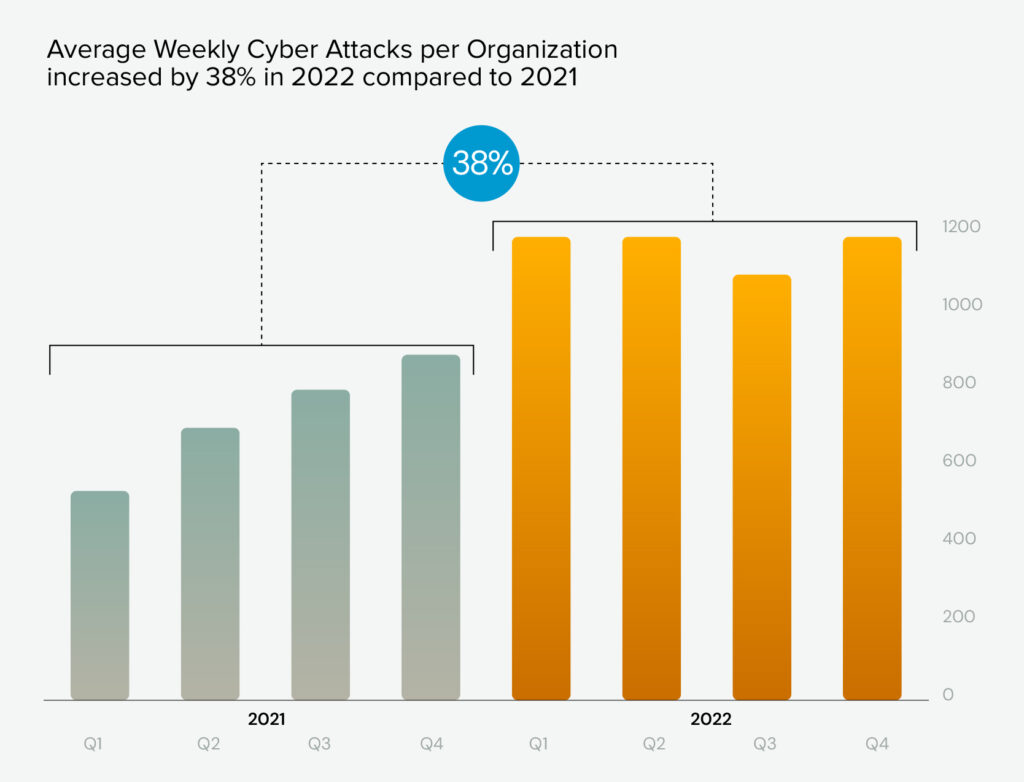
With cyberattacks increasing by 38% in 2022 alone, AI-powered security isn’t just a nice-to-have anymore — it’s a must.
In this article, we’ll walk through the top real-world use cases where AI in cybersecurity is making a real difference. Plus, we’ll show how Svitla Systems helps companies stay a step ahead with smart, flexible cybersecurity solutions.
Why AI Matters More Than Ever in Cybersecurity
Cyberattacks are getting smarter, faster, and harder to catch, and AI is quickly becoming one of the most essential tools in the fight against them. Unsurprisingly, the global market for AI cybersecurity is expected to grow from $24.8 billion in 2024 to over $102 billion by 2032. That kind of growth shows just how essential AI has become for keeping systems and data safe.
Unlike traditional tools, AI can sift through massive amounts of data, recognize unusual patterns in real time, and even respond automatically — often before anyone on the team knows there’s a problem. In fact, IBM reports that organizations using AI and automation can shave more than three months off the time it takes to detect and contain a breach, saving an average of $1.76 million per incident.
And it’s not just about reacting quickly. AI helps teams prevent attacks in the first place by scanning code for vulnerabilities during development, monitoring systems 24/7, and even predicting potential threats based on past behavior. You may be wondering if it is safe to automate cybersecurity. 61% of organizations now say they can’t keep up with advanced cyber threats without the help of AI. So, the answer is definitely yes.
At Svitla Systems, we help businesses make the most of what AI offers — from more intelligent threat detection to building more secure software from the ground up.
Key Examples and Use Cases of Cybersecurity AI
Use Case #1. Threat Intelligence and Predictive Analytics
Artificial intelligence has become a game-changer in cybersecurity — especially when it comes to staying ahead of potential threats. But how exactly does AI help prevent cyberattacks? One of its biggest advantages is its ability to keep an eye on everything in your IT environment — from devices and users to apps and how they all interact with your core systems.
By combining that asset inventory with threat data, AI can highlight the areas most likely to be targeted. It doesn’t just show you what’s wrong — it helps you understand where to focus your attention.
The real value is in how fast and widely AI can process information. It pulls data from different sources, makes connections humans might miss, and gives security teams a real-time view of their risk posture. That kind of visibility helps you catch threats early and respond faster, before damage is done.
Real Life Example
At PayPal, AI is key to keeping users and transactions safe. One major area is fraud detection. With millions of transactions happening every day, it’s not realistic for humans to check each one. The AI scans them all in real time, flagging anything that looks suspicious.
PayPal also uses AI to spot and block malicious websites. As phishing tactics evolve, their systems constantly scan the web to catch harmful content and prevent users from landing on scam sites. It’s a smart way to stay ahead of attackers who are always trying something new.
Use Case #2. Security Operations and Automation
AI is changing how security teams work. Instead of digging through logs or chasing alerts manually, teams can now rely on AI to process huge amounts of data in real time, from network activity and user behavior to endpoint signals. That means threats get spotted and handled faster. IBM reports that AI can cut detection and response times by as much as 14 weeks. That’s not just impressive — it’s practical.
AI also helps by scanning systems for weaknesses on its own. It flags the most urgent issues, suggests what needs patching, and reduces the manual effort it takes to stay on top of vulnerabilities. IBM’s security team, for instance, used AI to automatically close 70% of alerts and cut their response times in half within a year.
Automation is about helping people. By offloading repetitive tasks, AI gives security teams more time to focus on strategy and bigger-picture defenses. It also lowers the chance of mistakes that can happen when people are under pressure or overloaded.
Real Life Example
Plaid uses machine learning to handle identity verification. When someone connects a bank account, their system checks details like name, address, and Social Security number. It all happens behind the scenes and takes just seconds. That speed and accuracy help prevent fraud without slowing down the user experience.
Use Case #3. Advanced Threat Response and Mitigation
AI goes beyond just finding threats — it also helps respond to them quickly and smartly. By automating much of the reaction process, AI reduces the workload on security teams and speeds up how problems get handled. It digs through huge amounts of data like logs, network traffic, and global threat alerts, then acts on what it finds without waiting for human input.
That means the moment something suspicious appears, AI can instantly block harmful traffic or isolate infected files, stopping threats from spreading and causing more damage. This lets security teams move faster, make fewer mistakes, and keep the whole system safer.
Real Life Example
Wells Fargo relies on an AI-powered system that watches over their network, emails, and files all the time. It uses machine learning to pick up on unusual patterns that might signal an attack. When the system spots something, it acts quickly — blocking bad traffic or isolating risky files — to protect the company before things get worse.
Use Case #4. Smarter Vulnerability Detection and Management
Cyber threats are constantly evolving, and new vulnerabilities show up faster than security teams can keep up. AI helps change that. Instead of relying only on known risks, AI-powered tools like User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) watch for unusual behavior in real time — across devices, users, and systems — helping teams spot threats before they turn into real problems.
Real Life Example
Splunk’s Enterprise Security platform takes in data from across the organization — network logs, system events, user actions — and uses machine learning to look for patterns that don’t belong. It’s not just about flagging potential threats; it’s about making sure the most serious ones are handled first.
That kind of smart prioritization helps teams focus on what matters most, patch faster, and reduce risk without getting buried in alerts.
Use Case #5. User Behavior Analytics
One of the most powerful ways AI helps in cybersecurity is by learning how users and systems normally behave — and then noticing when something’s off.
Instead of relying on fixed rules, AI models watch how users interact with systems over time. They learn what’s typical — like when someone logs in, what data they access, or how they move through the network. When something unusual happens, like a login from a strange location or unexpected spikes in activity, AI can catch it quickly and alert the security team.
What makes this even more effective is that the models keep learning. The more data they analyze, the better they get at spotting actual threats versus false alarms.
This kind of behavioral analysis is also a huge help for proactive security. It gives companies a clearer picture of what’s going on across users and devices, so they can identify and respond to risks before they turn into real problems.
Real Life Example
CrowdStrike was one of the first to use behavioral analysis effectively in cybersecurity. Instead of only looking for known threats (indicators of compromise), they pioneered indicators of attack (IOAs) — a way to detect suspicious behavior before damage is done.
Their cloud-native Falcon® platform analyzes trillions of data points to spot patterns tied to attacker behavior. With the help of AI, CrowdStrike can now create new IOAs even faster, helping organizations detect and stop new, never-before-seen threats as they happen.
Conclusion
Cyber threats aren’t slowing down — they’re getting faster, smarter, and harder to spot. Traditional tools just can’t keep up anymore. That’s where AI really shines. It helps detect issues in real time, cuts down on noise, and takes the pressure off security teams by handling the repetitive, time-consuming tasks.
But more than that, AI and cybersecurity help you stay ahead. It gives you a clearer view of what’s going on in your systems, helps catch problems before they turn into something bigger, and supports better decision-making across the board.
Want to see how AI can work for you? Get in touch with Svitla Systems today — let’s protect your business together.



![[Blog cover] Top cybersecurity issues in healthcare](https://svitla.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/Blog-cover-Top-cybersecurity-issues-in-healthcare-560x310.jpg)

