Roughly every 10 years a new major technology emerges: mobile, cloud, and now artificial intelligence (AI). Some immediately jump on the bandwagon, only to realize that the adoption path is much harder than anticipated. Others prefer to wait and see the possibilities first before piloting the technology.
Compared to other sectors, retail has been on the more cautious side. In 2024, 42% of companies have already deployed AI at least in some capacity, and another 34% are at the assessment or pilot stage, according to an NVIDIA survey.
If you too are assessing whether it’s time to ‘upgrade’ for retail big data analytics to a more “intelligent solution”, this post is for you. Learn about the feasibility and advantages of AI implementation in e-commerce from the early pioneers.
6 AI Use Cases in E-commerce from Top Retailers
A quick online search, and you’ll get thousands of ideas on what AI can do for online retailers—automate warehousing operations, provide customer support, optimize inventory, or prevent fraud.
Yet, only large retailers can afford to trial different AI use cases before settling on the optimal selection. To save you time on research, we’ve lined up six areas where AI solutions can generate the best returns.
Customer Experience Management
Shoppers aren’t short on options, more so online. In a few quick taps (or even a voice command), they can discover goods in every category at every price point and seamlessly compare their options. One in two consumers already struggle to distinguish products from different brands. What persuades online buyers to choose one retailer over the other is customer experience.
Customer experience (CX) is the sum of every interaction shoppers have with your brand from the moment they discover a product until they’ve placed an order and received their shipment. Because online customer journeys are complex in retail, many things can (de)influence purchase decisions.
Globally, 6 in 10 shoppers will abandon their shopping cart when their preferred payment method isn’t available, a DHL survey found. For 95%, the choice of delivery options is also critical. Moreover, three-quarters of shoppers expect seamless interactions across channels with the support staff.
Data analytics helps online decipher complex customer behaviors, identify common points of friction, and optimize omnichannel experiences to improve engagement, conversions, and brand loyalty.
Online marketplace Zalando was among the first ones to implement a customer-centric approach to AI adoption. Its robust machine learning platform was designed to accommodate low-latency, high-volume data processing to support the company’s advanced on-site search experience.
In 2018, the retailer was among the first to introduce visual product search. Customers can upload trending looks or reference items and find the same or similar matches in the catalog, all thanks to a deep learning model. Later on, Zalando built extra features like more accurate natural language processing to account for misspelled words and better understand different types of user queries.
A year later, the retailer released an Algorithmic Fashion Companion (AFC) — a conversational assistant trained on outfit submissions from Zalando stylists, hired content creators, and data on past customer purchases to dish out unlimited, free outfit advice. Thanks to AFC, Zalando can better market products from its jumbo-sized product catalog of 1 million+ choices from more than 4,500 brands. The new tool did not just improve CX. AI product recommendations also drove 40% larger basket sizes and 2X higher conversion rates compared to single items, according to the company. The tool also provides personalized sizing recommendations, reducing the return volumes.
As generative AI went mainstream, Zalando’s engineers were quick to update the on-site assistant with new features. Now powered by a combination of proprietary ML and DL models and OpenAI’s LLM, Zalando Assistant can understand a wider range of user queries, provide better product recommendations, and even show locally trendy outputs with the Trend Spotter feature.
Zalando’s focus on deploying artificial intelligence in e-commerce to create a delightful CX is paying off big time. In Q3 2024, the marketplace reported a 7.8% increase in gross merchandise volume (GMV) both across B2C and B2B sales, generated by 50.3 million active customers.
Even better news? Zalando’s case isn’t unique. Incisiv found that globally, 54% of online
shoppers are more likely to complete a purchase after a personalized support session, powered by AI and data analytics. This means other retailers can achieve similar improvements in KPIs by investing in AI and machine learning solutions for e-commerce.
Demand Forecasting and Inventory Management
Retailers are now facing a problem of their own making. The average fashion trend cycle used to be twenty years. Today, a hyped trend hardly lasts for two months.
Fast fashion brands have set a high bar of releasing up to 52 “micro-seasons” collections each year. Social media and influencer marketing, in turn, hype the excitement for new trendy products and create new viral microtrends, often leading to overconsumption. Globally, social media users tend to purchase cosmetics, food and beverages, house appliances, and health supplements more frequently compared to less active peers.
With public preferences changing in a matter of scroll, retailers struggle to forecast demand and optimize their supply chain. After viral TikTok posts, 70% of retailers experienced stockouts and shipping delays, leading to frustration among shoppers.
Already facing tight profit margins, many retailers cannot afford to hold large inventory due to rising warehousing and product handling costs. At the same time, traditional demand forecasting methods cannot always alert about sudden spikes in demand, making stockouts a $1 trillion problem for retailers.
Soundly, new demand forecasting AI solutions for e-commerce promise to bring greater precision into inventory management. Capable of processing vast datasets in real-time, AI-powered demand systems can detect early shifts in customer sentiment, behaviors, and affinity for different products. Unlike traditional systems, they can also discover more correlations between different digital and physical events (for example, predict demand for aircon units using weather data).
With better demand insights, online retailers can optimize their inventory management: maintain optimal stock levels for different product categories, streamline replenishment, and improve assortment management.
Take it from OTTO, Germany's largest online store. The company uses artificial intelligence to keep inventory levels in check and prevent items from being purchased in excess.
The algorithm uses historical sales figures, customer behavior, seasonal trends, public holidays, weather, and planned marketing activities to estimate the impacts on sales volumes. It churns about 30 billion individual forecasts for the next 450 days for 2.5 million items each month, informing OTTO’s procurement quantities. The system also helps optimize logistics operations to ensure in-demand products are always in stock. 35% of OTTO’s product ranges are automatically reordered by the algorithm.
Product Merchandising
In-store or online, merchandising is the crux of successful retail sales. But managing thousands of SKUs across markets and customer segments is an intense job. Especially, when most teams have an accurate indication of inventory across their entire operations 68% of the time.
Facing data silos and accelerated sales cycles, merchandisers often struggle to deliver personalized marketing, launch impactful promotion campaigns, and adjust pricing to suit different customer segments. In its 2025 State of Fashion report, McKinsey notes retailers will need to “localize their go-to-market models, broaden their price ranges, and focus on brand positioning” to reach new profitable audiences and increase profitability.
“Shoppers who were once dazzled by the seemingly endless selection available at many online retailers now bemoan the difficulty of finding what they want. AI-powered curation, content, and search can help customers discover brands and products more effectively – and feel more inclined to make a purchase” – McKinsey, the 2025 State of Fashion report
AI merchandising systems enable ultra-personalization, based on browsing patterns, purchase history, and even contextual factors like location or time of day to deliver hyper-relevant product suggestions. These systems can dynamically adjust promotions or highlight best-sellers, helping online retailers increase conversion rates, maximize cross-selling opportunities, and create more engaging experiences that feel genuinely curated for each customer.
Luxury online retailer Farfetch uses AI models to optimize product presentation to different customer segments. The recommended system was trained on a combination of past customer interactions with specific products and product features in the catalog. By analyzing on-site behaviors in real-time, the system can immediately fetch suggested upsells, cross-sells, or similar items, based on the ranking scores, assigned to each product in the catalog.
“Three years ago, we really recognized that personalization was a key strategic initiative for us and we increased the size of our machine-learning data science teams and really invested in the talent to build on this type of technology. And it has really paid off,” shared CEO José Neves. Despite the overall dip in luxury spending, Farfetch managed to continue growing its user base and increased its profits to $748 million in Q2 2024.
Smaller online retailers, focusing on such AI use cases in e-commerce are also seeing strong returns. UK fashion brand Oh Polly invested in an AI-powered merchandising tool last year. By applying better category page merchandising tactics, the team drove a 270% increase in clicks and an 80% increase in conversion rate for its store.
Dynamic Price Optimization
Since the start of the decade, the retail sector has been on a rollercoaster ride. Sales volumes grew dramatically during the pandemic (and right after re-opening) thanks to economic stimulus. But then went down in 2023, following increased inflation.
The US National Retail Federation expects retail sales to increase by 2.5% to 3.5% by 2024, compared to 2023.
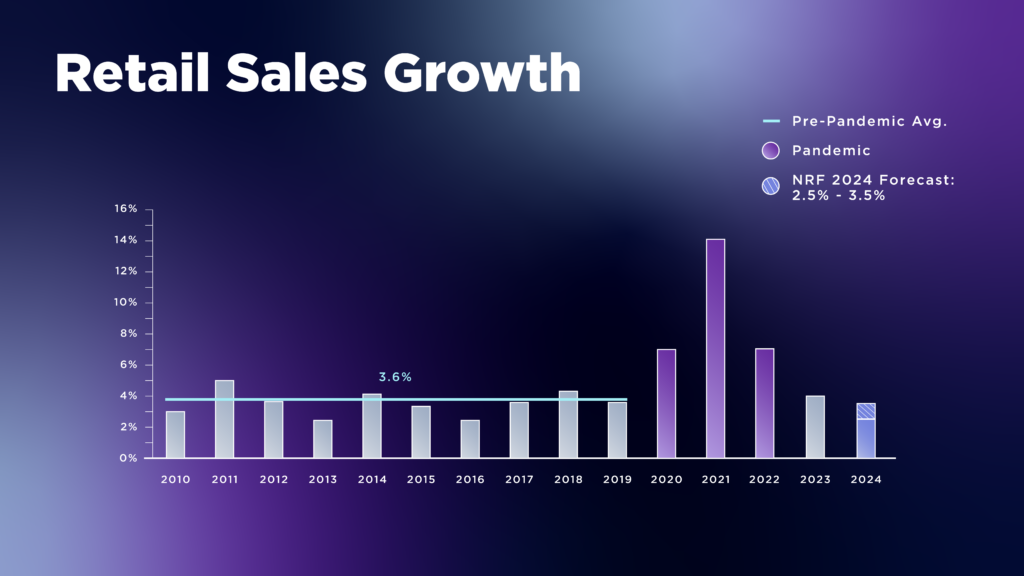
Globally, 64% of consumers remain concerned by inflation, according to a PwC survey. The volatile economic conditions result in decreased discretionary spending and greater price sensitivity.
For online retailers, pricing decisions are often further complicated by tight competition (comparison shopping is on the rise) and diminishing profit margins due to higher logistics and advertising costs. To find the right balance between underpricing (and sacrificing margins) and overpricing (and risking customer churn), retailers turn to dynamic pricing strategies.
Adaptive advertising, promotions, and pricing’ became the second top AI use case in retail, both among omnichannel and digital-only retailers according to an NVIDIA survey. Intelligent pricing algorithms can automatically adjust prices, based on a variety of market signals: demand, supply, competitor prices, changes in the weather, and overstocked levels, allowing retailers to differentiate prices by channel without hurting customer perception or profit margins.
British DIY retailer B&Q uses AI to effectively manage markdown and clearance pricing and offer personalized promotions to shoppers. US grocery chain Kroger also uses adaptive algorithms to maintain more competitive prices, based on the marketing dynamics.
Recently, however, dynamic pricing has caught some slack from consumer rights protection groups. But it isn’t necessarily a bad strategy. By using pricing intelligence, retailers can move inventory better to avoid deadstock or fresh produce perishability, which are both unsustainable. For example, dynamic pricing of grocery items and dynamic price reduction on perishable items, approaching their expiration date, can reduce food waste from grocery retailers by 21%. In the food industry, dynamic pricing decisions for food deliveries allowed the restaurant to generate more revenue while selling its meals for a lower price on average.
Order Fulfillment
Online shoppers have a low tolerance for long order fulfillment. They expect fast (and preferably free) shipping for most products within 2.15 days on average. Same-day and next-day shipping also remain an in-demand option.
Yet, many retailers struggle to meet these demands as they continue to face labor shortages and skyrocketing logistics costs. To run a leaner fulfillment function companies are experimenting with both retail workforce optimization, new fulfillment models, and digital technologies.
Electronics retailer Best Buy has 62% of e-commerce small packages shipped from automated distribution centers. As its online sales volumes grew, the company invested in the latest generation of warehousing solutions. Its regional warehousing centers have a fully automatic flow for managing order flows across conveyor belts and coordinating transportation between storage, picking stations, and shipping areas.
The robotics systems dramatically improved the overall speed and efficiency of order fulfillment, allowing later cut-off times and next-day deliveries without putting as much toll on human staff. Through a connected analytics dashboard, the system also saves frontline staff thousands of hours on shelves restocking in-stores as all goods arrive pre-sorted in totes.
Pharmacy chain CVS, in turn, relies on AI-powered fulfillment centers to fill over 2.3 million prescriptions each week across 29 states. The company says it’s using intelligent automation technology and machine learning for more effective workload allocation across its network of decentralized fulfillment centers.
Last-Mile Delivery Optimization
Last-mile delivery, getting an online order to customers’ hands, is another area where online retailers are feeling a tight price squeeze. Late last year, UPS and FedEx announced a 5.9% average rate increase on different shipping services. That’s when last-mile expenses already make up 53% of the total supply chain costs in retail.
Traffic congestion in large urban areas, limited parking, inaccurate delivery information, and frequent customer absences, also contribute to the challenges of creating smooth last-mile delivery windows. Moreover, lengthy detours increase retailers’ carbon footprints.
So AI usage for logistics and transportation is increasing, especially among larger e-tailers, who operate their own delivery fleets. Route optimization algorithms can dynamically update drivers’ daily routes, based on traffic data, weather conditions, and changes in delivery windows.
Walmart was one of the earliest adopters of AI-driven fleet management in retail and now offers access to its proprietary system to other businesses. The company’s Route Optimization system can automatically create multi-stop delivery journeys, based on parameters like time, location, and store delivery windows.
At the same time, such AI-powered last-mile systems an also provide real-time shipping updates to customers to reduce the odds of missed delivery and improve customer satisfaction.
Benefits of AI in E-commerce
AI implementation in e-commerce assumes major financial investments, spanning software, business process re-engineering, data security, and staff training.
So it’s important to understand the potential ROI of AI and communicate that data to others. Here several data points we find particularly persuasive for getting a buy-in:
- Better personalization. Online retailers, offering personalized experiences and support across channels enjoy 47% higher conversions. AI algorithms can produce hyper-personalized product suggestions, while Gen AI provides a better interface for content and product range discovery.
- Optimized profit margins. With a triple squeeze of growing logistics costs, reduced discretionary spending, and wage increases for talent retention, online retailers need to maximize their profitability. Adaptable pricing strategies help increase sales volumes through targeted promotions and average order values through savvy upsells and cross-sells.
- Higher operating efficiencies. 53% of retailers say AI adoption has improved operational effectiveness by eliminating manual or redundant workflows, improving access to data, and reducing work coordination complexities.
- Smarter logistics: AI systems can help optimize supply chain management, automating replenishment tasks, based on real-time data on inventory levels and demand trends. For last-mile deliveries, AI provides extra insights for route planning, leading to faster shipping times and reduced operational costs.
The bottom line: Both retailers and their consumers benefit a lot from smoother, more delightful experiences AI systems help create across the entire retail chain. Svitla Systems AI and machine learning team would be delighted to further introduce you to the possibilities of AI implementation in e-commerce. Contact us for a consultation.

![[SM cover] AI implementation in e-commerce](https://svitla.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/SM-cover-AI-implementation-in-e-commerce-936x527.jpg)


