Without a doubt, there was a substantial rise in the number of cybercrimes committed during the previous years. For instance, attacks on a global scale increased by 28% from Q3 2021 to Q3 2022, with more than 15 million records compromised. Also, cybercriminals' malware, phishing, and data theft techniques are continuously evolving and growing more sophisticated, putting organizations in a very tough place.
Before looking ahead, it's wise to look back. The most important cybersecurity events of the last year made for a disconcerting 2022. The mayhem that surrounded security teams was amplified by the fact that there are growing numbers of unfilled cybersecurity jobs, depleted staff struggling to deal with an expanding remote workforce, an expanding cloud, edge computing, and IoT universe, growing interconnectedness, and increased consequences of digital acceleration, to name a few.
As we put the pedal to the metal for 2023, we can already see the potential threats that will emerge in the cyber realm this year such as identity compromise, high-stakes ransomware, high-profile phishing, and more.
To prevent hackers from gaining access to sensitive information or damaging essential infrastructure, governments and organizations have established stricter cybersecurity policies and guidelines. Companies in the private sector have stepped up their inspections of supply chains in an effort to spot vulnerabilities like embedded credentials and mismanaged sensitive data. Cyber insurance companies have been under a lot of strain recently, so they've increased their already stringent standards. Undoubtedly, significant changes are on the horizon.
In this article, we debrief you on the most exploited vulnerabilities that cyber attackers love to target as well as the top cybersecurity threats to be on the lookout for in 2023. And should you be interested to know how Svitla Systems handles security needs and ongoing security improvements, we recommend this article for deeper insights.
Why Does Cybersecurity Matter for Any IT Project?
Cybersecurity prevents malicious actors from gaining access to sensitive information and devices. For IT and security professionals, cybersecurity entails monitoring networks for malicious activity, identifying potential threats, and responding to any actual attacks. Because new cybersecurity threats emerge at a rapid pace, cybersecurity measures must evolve to stay one step ahead of cybercriminals and their attacks. Nowadays, practically all company operations take place online, which means that all cybersecurity measures must extend to a wide variety of online environments.
All kinds of data can be stolen or damaged, making cybersecurity a crucial endeavor for all organizations, private or public. All sorts of information, including medical records, social security numbers, names, addresses, and credit card numbers, as well as intellectual property, data, and government and commercial information systems, fall under this category. Companies lacking a robust cybersecurity program are easy targets for cybercriminals as they are rendered helpless against data breach attacks.
Due to growing interconnectedness and the rise of cloud storage services like Amazon Web Services, both inherent risk and residual risk are growing. In parallel, the likelihood of a successful cyber attack or data breach is increasing due to the widespread design weaknesses of commercial cloud services and the increasing sophistication of cyber thieves.
Business executives can no longer rely on "out-of-the-box" cybersecurity solutions like antivirus software and firewalls, as hackers are growing more sophisticated and their strategies are becoming more resistant to traditional cyber defenses. To ensure complete safety, it's crucial to take an all-encompassing approach to cybersecurity detection, protection, response, and remediation.
Social engineering scams, phishing, ransomware attacks, and other viruses meant to steal intellectual property or personal data should all be part of a company's mandatory cybersecurity awareness training.
Information security is no longer limited to highly regulated sectors like healthcare and financial services due to the prevalence of data breaches. Damage to a company's reputation caused by a data breach can be permanent, even for a startup operation.
Cybersecurity Statistics in 2023
- Cybercrime is slated to generate $8 trillion in damages in 2023.
- The global cybersecurity market is worth $173.5 billion.
- The global cyber insurance market is worth $9.2 billion approximately.
- More than 57% of organizations claim a cybersecurity skills shortage.
- The average cost of a data breach is $4.24 million.
- 31% of organizations cite compliance as a roadblock in migrating to cloud infrastructure.
- There will be 3.5 million unfilled cybersecurity jobs in 2023.
- Data privacy regulations only protect the data of 65% of the world's population.
- 20% of managers claim to have experienced a data breach as a result of remote workers.
- More than 95% of cybersecurity breaches happen because of human error.
- Over 25% of all employees have noticed an increase in fraudulent emails, phishing attempts, spam, and more, since the beginning of the pandemic.
- There are 2,244 cyberattacks per day, equating to over 800,000 attacks per year. That's almost one attack every 39 seconds.
Top Cybersecurity Threats in 2023
Human Error & Untrained Staff
When it comes to cyber security, some of the top cybersecurity threats and most exploited vulnerabilities to companies typically come from within. Researchers at Stanford found that human error—whether deliberate or unintentional—accounted for 88% of all data breaches. The failure of businesses to provide adequate security training is a leading cause of data breaches caused by accidental disclosures made by employees.
In 2022, for instance, phishing emails were the most common type of risk to cybersecurity that people fall for. What might possibly be the cause of this? Email is often used for phishing scams, and many of them include harmful attachments or pretend to be reputable businesses or persons to trick users. Staff members who have not been adequately educated on how to recognize and avoid phishing attempts are not likely to take precautions. This leads to cyber attacks that cause significant damage.
Many employees lack the expertise to recognize a phishing email, which is becoming increasingly important as assaults get more complex. Businesses should create cybersecurity risk management policies and hold training sessions to inform workers about the nature of cyberattacks, how to recognize them, and what to do to prevent them from succeeding.
Pro tip: Organizations must keep investing in cybersecurity training. Overexplain to employees why cybersecurity affects everyone and how to follow protocols instead of workarounds. Train teams regularly and deploy tests to keep people vigilant.
Ransomware
All businesses, no matter how big or small, face a significant risk of cybersecurity from ransomware in 2023. If your network is infected with ransomware, your data and computers will be locked down until you pay the criminal a ransom. Cyberattacks have a multiplicative effect on corporate losses, including monetary ones, as well as losses of data and lost productivity. Loss of commercial possibilities because of data inaccessibility can be detrimental to a company's bottom line, especially if the attack lasts for an extended period of time.
We can expect ransomware assaults to continue for the foreseeable future. The United States Department of Homeland Security reports a worldwide rise in ransomware assaults. This type of attack has become common since hackers don't require a lot of expertise to pull it off. Until recently, only the most skilled hackers were able to launch successful ransomware campaigns. Nonetheless, "Ransomware-as-a-Service" kits are becoming increasingly accessible for use by less experienced hackers. Because small businesses typically have less sophisticated cyber security architecture and these kits require little-to-know technical hacking expertise, they were originally developed to target small businesses.
Pro tip: Emphasize the importance of cybersecurity expertise and best practices at the organizational level and create structured cybersecurity plans to combat ransomware attacks.
Hybrid Attack Tactics
There may be major shifts in the threat actor landscape as a result of the blurring of lines between previously distinct types of threat actors. State-sponsored actors have begun using cybercriminal techniques like ransomware coupled with DDoS or malware to compromise vital infrastructure.
Pro tip: Researching every data point can be challenging for human staff, which is where artificial intelligence comes in to not only detect even the slightest anomaly but also learn new, hybrid malicious moves from cyber attackers.
Failure to Manage Top Cybersecurity Threats
The most effective technologies for preventing cyber attacks, such as two-factor authentication (2FA), endpoint security, and cloud-based solutions with automated encryption, are often overlooked by businesses. A major missed opportunity, given the effectiveness of these safeguards in reducing exposure to common forms of cybercrime like phishing and social engineering.
Lack of proper cyber risk management not only leaves companies vulnerable to cyber attacks, but it can also make it difficult for them to obtain adequate cyber insurance. Acquiring new cyber insurance policies and renewals has become increasingly challenging in recent years due to the rising frequency of cyberattacks.
Pro tip: Use cyber risk management strategies that account for both current and future top cybersecurity threats and employ tools on platforms that leverage the latest technologies such as artificial intelligence, deep learning, and machine learning for early threat detection and protection.
Unprotected Internet of Things Devices
The Internet of Things (IoT) encompasses a global network of millions of interconnected devices. Many individuals and businesses are taking advantage of IoT technology but due to the internet's increased accessibility, hackers have a backdoor to sensitive information. IoT devices provide an entry point into a network, allowing hackers to hold users' data hostage in exchange for a monetary reward. Experts agree that rapid enterprise use of IoT technologies makes IoT one of the most pressing future cybersecurity concerns. Network-connected hardware always has the chance of being compromised.
Pro tip: When dealing with security holes, it is essential to keep a close eye on IoT devices and update their security firmware as soon as patches become available. Passwords that are too simple to crack are another cause of Internet of Things hacks. Password-protecting IoT devices and using multi-factor authentication become essential.
Patches as an Afterthought
The use of outdated software is a popular entry point for cybercriminals. Why? Because insecure data is left exposed and outdated software is a weak point in device systems. In this way, businesses and organizations might fall prey to a wide variety of cyber-attacks if they fail to maintain up-to-date software. As soon as an exploit is discovered, cybercriminals typically use it to launch an attack.
Pro tip: Avoid cyberattacks by keeping your software up-to-date and being proactive about system patches.
Social Engineering
Deception is at the center of every social engineering attack, which uses social interactions to get access to sensitive data. Cybercriminals rely on trickery and manipulation to steal sensitive information, circumvent security measures, and reveal private details. The three most common forms of social engineering attacks are phishing (sending emails containing malicious links), baiting (leaving compromised devices in public), and scareware (i.e. using scare tactics to lure users into buying infected software).
Pro tip: Ensure your staff is aware of recent social engineering attacks and teach them to handle and report suspicious behavior. Use VPNs to prevent outsiders from intercepting your networks and constantly monitor them.
Cloud Breaches
The more sensitive information is stored on the cloud, the greater the risk of a massive security breach. Cloud storage's popularity has soared over the past several years, but as more sensitive data is stored there, so too has the determination of cybercriminals to find a method to steal it. Several types of cyberattacks can compromise cloud services and make it impossible for organizations to access their data. In an effort to safeguard sensitive information, many companies are turning to cloud security solutions, which have gained popularity in recent years due to the assurance they provide. Although technical safeguards are important, they are not the complete answer.
Pro tip: Re-check your cloud configuration, share data on a must-know basis, and protect credentials by implementing multi-factor authentication and encryption.
Third-Party Entry Points
Payment processing platforms or secure file-sharing platforms are just a couple of examples of the plethora of third-party services used by today's organizations. Without them, it would be difficult to maintain company efficiency. Despite the obvious advantages, many businesses fail to adequately address the risks associated with using third-party services. Third-party vendors being the targets of cyberattacks is unfortunately not an unusual occurrence. But, is your company shielded from personal liability in the event of a breach by a third party your company contracts with? Sadly, chances point to no.
Personal information, such as customers' social security numbers and credit card details, may be at risk even if a company doesn't handle it directly.
Pro tip: Organizations should conduct regular vendor risk assessments to reduce the likelihood of a security breach caused by a third party.
Outdated Hardware
Using out-of-date hardware is a common tactic used by hackers to get access to small, medium, and large organizations. Why? Simply said, hackers can easily attack security flaws in outdated gear since it lacks the most up-to-date software, which typically includes the latest security patches.
Pro tip: As with software, it's important to update hardware regularly. The long-term cost savings of mitigating cybersecurity attacks make the investment in user-friendly new hardware worthwhile.
Most Exploited Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities 2023
A holistic and robust level of protection can only be attained by having a deep understanding of cybersecurity vulnerabilities and the methods employed by threat actors to penetrate networks. Cybersecurity vulnerabilities can arise from any weak spot in an organization's internal controls, system procedures, or information systems.
Cyber attackers exploit these vulnerabilities to gain authorized access to networks, posing a significant risk to confidentiality. Nowadays, information is like a treasure trove, so it's crucial to keep it safe at all costs. Therefore, it is critical to conduct regular checks for cybersecurity vulnerabilities, as network weaknesses might result in a full breach of an organization's systems.
Some common types of cybersecurity flaws include:
- Failure to encrypt data
- Unavailability of surveillance equipment
- Permissionless distribution of potentially harmful files
- Files downloaded without first verifying their integrity
- Redirecting users to malicious websites via URLs
- Poor passwords that aren't changed
- Insecure websites
An exploitable vulnerability only requires a single, well-defined attack vector. Next, you can find some of the most damaging cybersecurity vulnerabilities of modern times:
- Log4Shell. The logging part of the Apache Tomcat server software has a vulnerability called Log4Shell. Originally found in 2021, this vulnerability sends a specially-crafted request so attackers can run any code on the server. In a later version of the Tomcat server, the vulnerability was fixed, but many systems hadn't been fixed yet and were still at risk.
- Zero-Day in Google Chrome. This vulnerability in the Google Chrome web browser was a zero-day exploit. It was found in 2022, and attackers could run any code on a user's computer if they could get the user to visit a malicious website. In a later version of Chrome, the vulnerability was fixed, but many users were still at risk until they updated their browsers.
- Spring4Shell: Spring4Shell is a vulnerability in the popular Java-based Spring framework, which is used to build web applications. It was found in 2022, and attackers could send a malicious request to the server to run any code they wanted. In a later version of Spring, the vulnerability was fixed, but many systems hadn't been updated and were still at risk.
- Microsoft Office Bug: This vulnerability was caused by a bug in the Microsoft Office suite. It was found in 2017, and attackers could run any code on the user's system if they could get the user to open a malicious file. A later version of Office fixed the vulnerability, but many users were still at risk until they updated their software.
- Atlassian Confluence RCE Flaw: The Atlassian Confluence collaboration platform was found to have this vulnerability. By sending a malicious request, attackers could run any code they wanted on the server. In a later version of Confluence, the vulnerability was fixed, but many systems hadn't been fixed yet and were still at risk.
- ProxyNotShell: ProxyNotShell was found in the popular proxy software HAProxy. They let attackers run any code on the server by sending a request that was specially made. In a later version of HAProxy, the holes were fixed, but many systems hadn't been fixed and were still at risk.
You can find a complete catalog of known exploited vulnerabilities curated by the Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) here.
What Are Cybersecurity Threat Maps?
Cybersecurity threat maps, also known as cyber-attack maps, are visual representations of the locations and types of computer security threats occurring in real-time. Think of them like a giant game of laser tag where different colored beams of light arc across a black background to indicate the direction and origin of an oncoming attack.
<Example - click on image - it's a link>
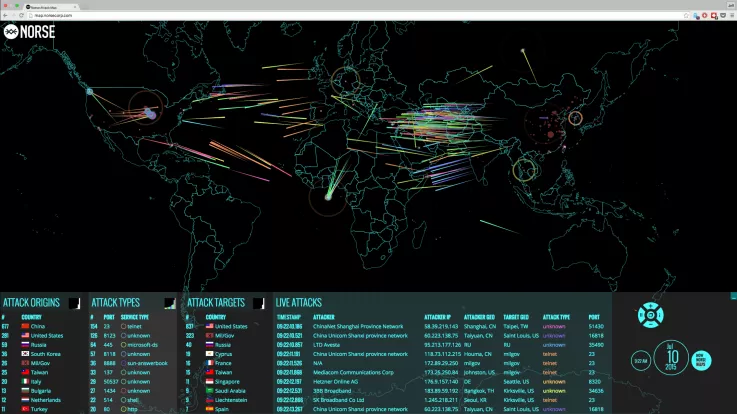
A cybersecurity threat map is a top-notch, visual representation of the current state of cyber threats that can be understood by anyone. For the average person, it may be as simple as realizing how commonplace these kinds of attacks are. Cyber security experts can use the information provided by a cyber danger map to identify new possible attacks.
Every day, millions of cyber threats strike unsuspecting victims, some of whom actively fight back, while others take preventative measures or take a passive stance. Most of these destructive actions are botnets whose sole purpose is to shut down infrastructures and cause havoc among corporations, while some of them are manually targeted cyber attacks.
Modern digital cybersecurity threat maps share these traits:
- Many of these maps only show historical data on previously completed attacks.
- They are narrowly focused on displaying DDoS assaults and don't cover any other forms of cyber attacks or threats.
- They display aggregate, anonymous statistics.
Cybersecurity in the Future
Every day, we can find the latest news about cybersecurity, and the picture looks bleak. Because technology has changed, the cybersecurity industry has grown. But a lot more growth and development are needed to deal with the growing number and complexity of possible threats.
Cybersecurity is a race that will never stop, but it's becoming faster and faster all the time. It's no secret that corporations are always spending money on new technologies. Now, in order to facilitate remote work, improve the customer experience, and produce value, they are adding new layers of infrastructure to their IT networks, which opens the door to a host of new security risks.
To cope with the modern challenges of cybersecurity, organizations need to partner with cybersecurity experts that employ the latest technologies and frameworks to protect their most valued assets. Svitla Systems provides consulting services and has ample expertise and know-how across the entire cybersecurity spectrum. We apply our knowledge to all web solutions and mobile apps we craft for our multiple customers.
For more information, please reach out to our experts who will be happy to provide all the information you need.





