While AI is going at full tilt and the future seems to be looming over too early, some critical sectors like healthcare are still dragging with their digital transformation.
Though the urge for digital solutions is apparent, healthcare has lower digital maturity compared to other industries. According to the World Economic Forum Report, “Most healthcare systems still have fragmented IT infrastructure, incompatible data standards and poor ways of sharing this data, and a patchwork of digital solutions, all of which hinder impact. ”
This Digital Acceleration Index compares digital maturity levels across 10 key industries in Europe, the US, and Asia. See what continent does its best with digital transformation in healthcare (HC).
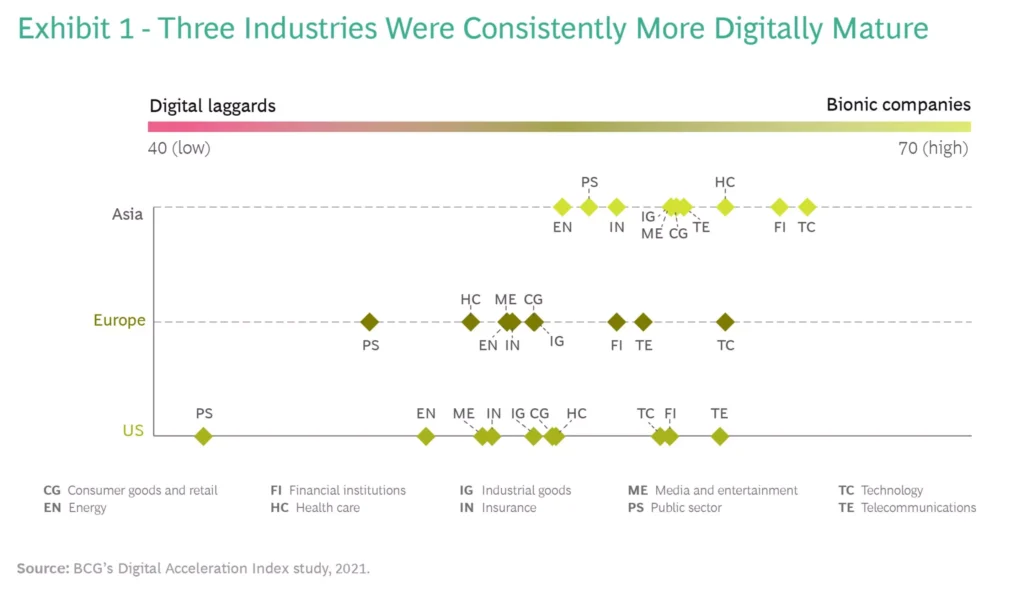
There are many root causes for such a gap in the implementation of advanced technologies—relying on legacy systems of most clinics and healthcare organizations (e.g., monolithic Electronic Medical Records), lack of standardization across workflows, ineffective and often impaired processes, limited budgets, resilience to change (typical “if ain’t broke, don’t fix it” approach).
On top of that, healthcare is also globally pressured by:
- Striking shortage of medical staff, specifically in low- and mid-income countries – up to 10 million by 2030 as per WHO
- Overwhelming administrative burden noticed by 87% of providers that often results in 28 hours per week taken from patients care time
- A high 20% spending waste rate in healthcare
- Booming chronic diseases – by 2050 they are expected to cause 86% of all deaths per year
- Unjust access to basic healthcare services – half of the world’s population has none.
Digital Solutions that Boost Patient Outcomes
The above problems have piled on hospitals, providers, and patients long before the lockdowns. However, since 2019, they’ve started jumping off the page, making healthcare organizations recognize and fight setbacks.
The shift to outcomes-focused healthcare is one of the approaches many organizations choose to address current challenges, revamp patient experience, and think beyond reactive measures.
One of the benefits of digital transformation in healthcare is that it has all the capabilities for a patient-tailored treatment. Here are some of the most well-developed digital solutions and top technologies that prompt positive patient outcomes and help address the most pressing challenges:
1. Telemedicine and Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
The good thing about telemedicine and RPM solutions is that now many hospitals and patients use them as part of their routine. Even after the pandemic receded, the demand for such solutions hasn’t plummeted. Just look: only in 2024, 78,6% of hospitals adopted a telemedicine app for online doctor consultations.
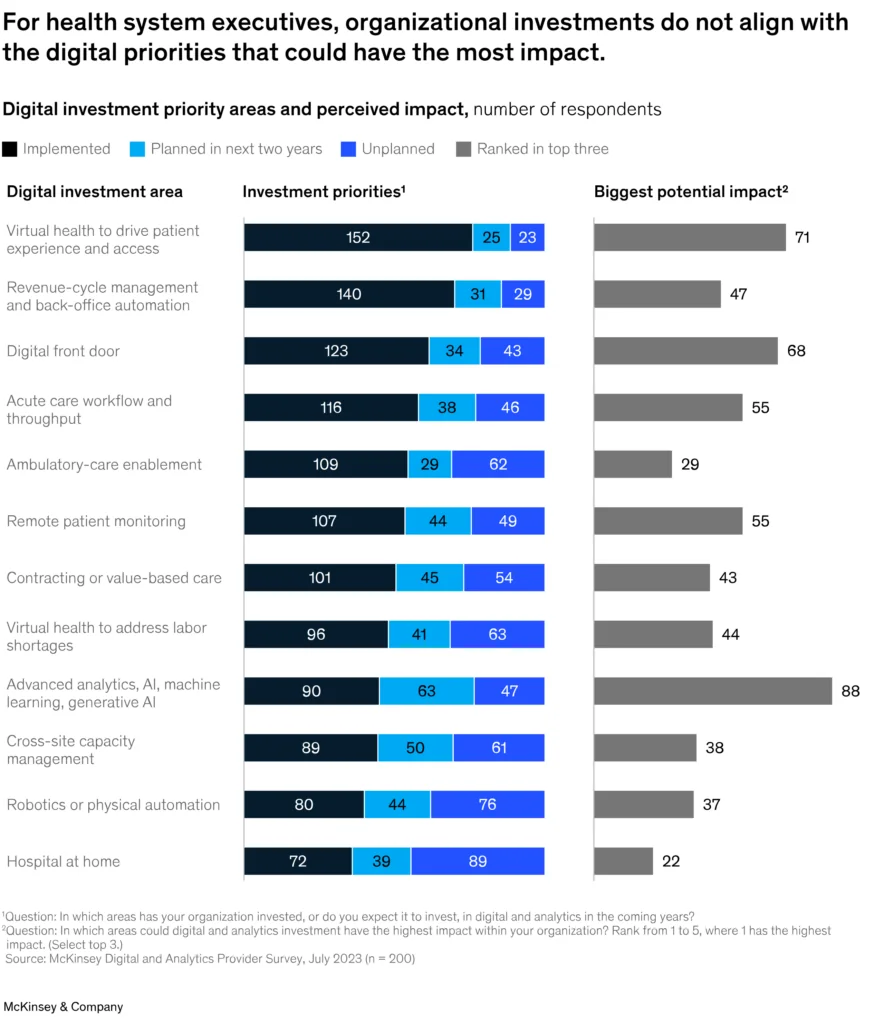
On top of that, they have grown to more comprehensive systems like virtual health apps (telemedicine for doctors together with AI diagnostics, chronic disease management, mental health apps, weight loss, etc.) and digital front door (telemedicine for patients within a customer-facing portal providing access to their data, doctors’ portfolios, lab results, appointment schedules, etc.). By the way, they are the top investment priorities for health system executives according to the McKinsey survey:
If you start looking for telemedicine app development solutions, you’ll probably notice how they put forward integration with RPM devices, which also prompts accessibility of medical services. Not only do they bring the needed medical assistance to those who live in remote and isolated areas, but they also help cut waiting times for people in overpopulated cities.
Both work with EHR systems to build up an ecosystem of interoperable digital solutions for remote diagnostics, monitoring, and treatment. Many telemedicine software providers (e.g., Teladoc, Amwell, MDLive, etc.) offer solutions that are well-compatible with such devices as pressure cuffs, heart trackers, glucometers, digital stethoscopes, pulse oximeters, activity trackers in wearables, etc.
While RPM devices gather data in real-time, telemedicine apps sync with the Electronic Health Records (EHR) system to use historical patient data, analyze collected intel, send alerts and notifications about a patient’s critical conditions to doctors.
Want to develop a custom telemedicine app that is well-integrated with your existing infrastructure? Check this most detailed Guide to Telemedicine App Development, which also explains the difference between telehealth and telemedicine.
2. Electronic Health Records System
This one is like a kernel of digital transformation in healthcare. Its market share is projected to grow to over US$ 49 billion from 2024 to 2029.
An electronic health record (EHR) system is a key database collecting all personal and medical data of patients and registering every step of their healthcare journey (treatment plans, prescriptions, lab results, etc.).
Clearly, the paperwork is out. Other than that, here goes more accurate and secure patient data management and sharing between different involved parties. An EHR system is more complex than standard Electronic Medical Records (a patient chart accessed only by one provider). It supports the coordination of efforts of paramedics, doctors, nurses, pharmacies, lab workers, healthcare providers, and all those contributing to positive patient outcomes.
Digitizing records and securing access to them put the healthcare system to a real test. Especially with all those data-related issues:
- Data inaccuracies and errors that negatively affect treatment and prescriptions for 33% of patients.
- Data storage and management issues – 49% of executives report dealing with siloed patient records across disparate systems
- For example, data duplicates – over 50% were found in 104 million records.
Each day one mid-sized hospital generates 137 terabytes of data. Processing and managing such data volumes should be continuously improved and automated to exclude the above matters.
3. Predictive Analytics and Artificial Intelligence
That is where AI and predictive analytics come in hand. AI and ML are believed (59% of respondents) to improve data accuracy, consistency, and reliability. Coupled with robust cloud-based data management platforms and real-time data processing engines, AI-powered digital solutions can handle large volumes of heterogeneous unstructured data.
On a broader scale, AI, accompanied by predictive analytics, helps doctors to reach correct diagnoses sooner. By using deep learning models, it discovers trends and defines patterns and anomalies using data from EHR systems, telemedicine apps, RPM devices, conversations between chatbots and patients, etc. For example, using AI-powered C the Signs tool the doctors of GP practices noticed that the cancer detection rate soared to 66% compared to 58,4% rate in those practices that didn’t use AI. By determining potential health risks and outcomes early, doctors bring precise treatment plans to patients faster. Using predictive models and advanced analysis of images, it’s also possible to tell the likelihood of genetic disease development or how the current disease progresses.
If you’re looking into other use cases of AI in healthcare, like drug development and automation of administrative jobs, then you should also see this article.
4. AI, IoT, and RPA Optimizing Administrative Jobs
What is the average time physicians and other medical staff spend on administrative tasks? One of the latest studies says it is from 28 to 34 hours each week. Among such tasks often are:
- appointment scheduling
- manual data collection (patient demographics, insurance) and consent forms
- medical notes entry
- prescriptions filling and verification
- billing
- insurance claims processing
- updating records
- shifts scheduling and payroll
- procurement and tracking of supplies and equipment, etc.
This list will be even longer for many large hospitals with multiple departments and services. This is why healthcare providers are looking into ways to minimize the negative impact of administrative burden, waste, and staff burnout.
One of such is the adoption of AI/ML, Predictive Analytics, Deep Learning (DL), RPA, and IoT. Here are their most common use cases:
- Automated appointment booking, adding patient data, history, lab results, and payment details to EHRs using RPA bots or AI-powered chatbots within a customer-facing app.
- AI, NLP, and OCR to analyze patient data and medical records, interpret image data, and automate the processing of insurance claims. Improving security and accuracy of a billing process, fraud and anomaly detection in payments.
- RPA can do anything connected to data extraction and entry, e.g., derive EHR codes for invoice generation, auto-fill claim forms, track their status, etc.
- Generative AI can assist nurses in crafting short summaries about patients.
- Improving inventory management by adding predictive analytics to forecast medical supplies availability.
- Predictive maintenance of medical equipment to detect issues and cut downtime.
- Optimizing supply chains with advanced AI-powered trends analysis, including ordering automation and allocation of resources per demand.
- IoT sensors embedded in hospital’s beds can help monitor their occupancy. Using RFID tags or IoT sensors, you can also track equipment and inventory (location, usage, etc). Moreover, medical staff can automate adjustments of environmental parameters like humidity, quality of air, temperature, etc.
- ML-based anomaly detection and automated compliance monitoring can help prevent unauthorized access or possible breaches. This will secure patient data and help track conformity with HIPAA regulations.
Challenges and Concerns Towards Digital Transformation
Digital transformation journeys often come with bumps along the way. Recognizing the pros and cons of telemedicine, EHRs, RPMs, AI/ML, and other technologies is one of the steps toward responsible digital transformation. This is why, before taking the plunge, weigh in on all possible challenges and how you will address them.
The latest McKinsey’s survey shows that many healthcare providers are most concerned with budget restrictions (50%) and legacy system modernization (33%) challenges.
Legacy software challenge: High cost for the legacy software upgrade and migration from on-premises infrastructure to the cloud scares off many digital initiatives. Therefore, providers should take a step-by-step approach, focusing on digitizing their healthcare records and some of the most overwhelming administrative tasks. Learn more how Svitla Systems approaches digital transformation with outdated systems.
Integration with other systems: Not only legacy infrastructure complicates integration between EHRs, RPMs, digital front doors, and other solutions. Lack of data unification and standardization, multiple systems and solutions from different vendors make data exchange and interoperability almost a conundrum. Using FHIR and HL7-compliant APIs can help establish effective data exchange between heterogeneous systems. While a cloud-based data platform with advanced analytics can handle vast volumes of different datasets and ensure real-time data processing.
Security and regulatory compliance: Though such regulatory laws as HIPAA and GDPR aim to fully secure PHI (Protected Healthcare Information), they also require additional measures (security, controls, data encryption, authentication, risk assessment, etc.) and administrative work (policy adherence, documentation, etc.). Consider ML-powered compliance monitoring tools, disaster recovery, and security operations solutions.
Final Thoughts
The healthcare industry is one sector that calls for digital transformation in every aspect. Yet, there are plenty of challenges, concerns, and new technologies to learn and adjust to multiple regulations. Request the help of a professional in digital healthcare services, to benefit the most from your investment in digital solutions.

![[Blog cover] Digital transformation technologies in healthcare](https://svitla.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/Blog-cover-Digital-transformation-technologies-in-healthcare-936x527.jpg)


