AngularJS has internationalisation (i18n) and localisation (l10n) out of the box. It just works with content that is generated via AngularJS Framework: date, currency, etc.
Sample of localization and internationalization for China
<script src="angular.min.js"></script>
<script src="i18n/angular-locale_zh-cn.js"></script>
<script>angular.module('myApp', [])</script>
<div ng-app="myApp">
{{578793600 | date:'longDate'}} <br />
{{2000 | currency}}
</div>
Code language: HTML, XML (xml)
To change locale to other language/country you need to insert locale file from: https://github.com/angular/angular.js/tree/master/src/ngLocale
For example, the same that is good to read for Ukrainian citizens — date format and month name.
<script src="angular.min.js"></script>
<script src="i18n/angular-locale_uk-ua.js"></script>
<script>angular.module('myApp', [])</script>
<div ng-app="myApp">
{{578793600 | date:'longDate'}} <br />
{{2000 | currency}}
</div>
Code language: HTML, XML (xml)
This mechanism that provides to us AngularJS framework is very primitive and there is lack flexibility for making application really international. No way to translate static text, custom filters.
Also, main disadvantages is an inability to change locale in run-time — you should somehow replace script[src] of locale and refresh page. It is not SPA way.
Luckily, in our-days, we have good 3-rd party solutions for application localisation such as angular-localization and angular-translate.
In this article let’s investigate and create the simple multilanguage application.
Solve main problems:
- Translate all text in application views and in async requests.
- Switch between languages in run-time, without refreshing the app.
- Detect device localisation to set default language individually.
- Remember which language has been chosen before.
Develop multi-language app using angular-translate
angular-translate in the most popular module for translation of applications. It is available on GitHub, well documented and stable with last Angular version.
Install
bower install angular-translate
npm install angular-translate
CDN: https://cdnjs.com/libraries/angular-translate
Init module
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en" ng-app="myApp">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<script src="angular.js"></script>
<script src="angular-translate.js"></script>
<script src="app.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome</h1>
</body>
</html>
Code language: HTML, XML (xml)In app.js file init myApp and add ‘pascalprecht.translate’ as a dependency.
angular.module('myApp', ['pascalprecht.translate']);
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Translation table
The simplest way is to take place for translation table in .config.
Translate Welcome to English and Deutsche.
Translation table for each language will be an object with a set of key, value. Where key — is an identifier in view and value — translation.
angular.module('myApp', ['pascalprecht.translate', 'ui.bootstrap'])
.config(function ($translateProvider) {
$translateProvider
.translations('en', {
'Welcome': 'Welcome'
})
.translations('de', {
'Welcome': 'Willkommen'
});
$translateProvider.preferredLanguage('en');
});
Code language: PHP (php)Set English as language by default.
<!-- Directive -->
<h1 translate="Welcome"></h1>
Code language: HTML, XML (xml)Update template using filter or directive. Almost all AngularJS style guides recommend avoiding filter because of productivity. But in some cases, filter can be the only way.
<!-- Filter-->
<h1>{'Welcome' | translate}</h1>
Code language: HTML, XML (xml)The structure of translation table can be more complex. Often translation depends on context. Button and title in English can be the same but on another language not.
Let’s add more elements in template:
<h1 translate="Welcome"></h1>
<p>Join 25,000 other subscribers today</p>
<h2>Subscribe</h2>
<div>
<input type="text" placeholder="Your Email">
<button>Subscribe</button>
</div>
Code language: HTML, XML (xml)Notice, that Subscribe text in the title and in button. Structure of translation table can look like:
Plain:
.translations('en', {
'title - Subscribe': 'Join 25,000 other subscribers today',
'title - Welcome': 'Welcome'
'btn - Subscribe': 'Subscribe',
})
.translations('de', {
'title - Subscribe': 'Heute 1000 anderen Abonnenten beitreten.',
'title - Welcome': 'Willkommen'
'btn - Subscribe': 'Abonnieren',
})
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)Nested:
.translations('en', {
'TITLE': {
'SUBSCRIBE': 'Join 1000 other subscribers today.',
'WELCOME': 'Welcome'
},
'BUTTON': {
'SUBSCRIBE': 'Subscribe'
}
})
.translations('de', {
'TITLE': {
'SUBSCRIBE': 'Heute 1000 anderen Abonnenten beitreten.',
'WELCOME': 'Willkommen'
},
'BUTTON': {
'SUBSCRIBE': 'Abonnieren'
}
})
Code language: JavaScript (javascript)For correct filter and directive working key value in the nested object should be without spaces. In the official documentation, there is a recommendation to name keys of the object in the table with capital letters and low dashes because it is constant. It’s important to spend time and decide about namespacing in each case.
Template in HTML will look like:
<h1 translate="TITLE.WELCOME"></h1>
<p translate="TITLE.SUBSCRIBE"></p>
<div>
<input type="text" translate-attr-placeholder="Your Email">
<button>{{"BUTTON.SUBSCRIBE" | translate}}</button>
</div>
Code language: HTML, XML (xml)What about a placeholder? For attributes, angular-translate has a specific directive.
<input type="text" translate-attr-placeholder="Your Email">
Code language: HTML, XML (xml)Notice that there is no “Your Email” in translation table — as default, the value will be as a value of directive (according to name convention key of this translation will be “YOUR_EMAIL”).
Result
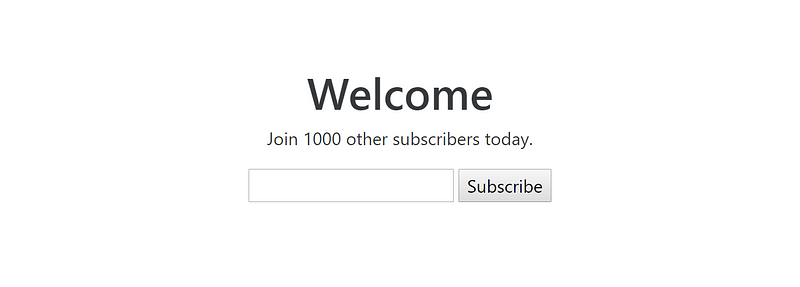
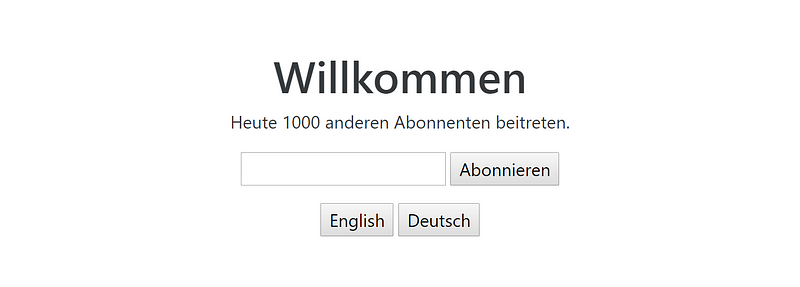
Set default language
In .config section add: $translateProvider.preferredLanguage(‘en’);In this milestone, we have already implemented translation functionality but still, have no controls.
angular.module('myApp', ['pascalprecht.translate'])
.config(function ($translateProvider) {
$translateProvider
.translations('en', {
'TITLE': {
'SUBSCRIBE': 'Join 1000 other subscribers today.',
'WELCOME': 'Welcome'
},
'BUTTON': {
'SUBSCRIBE': 'Subscribe'
}
})
.translations('de', {
'TITLE': {
'SUBSCRIBE': 'Heute 1000 anderen Abonnenten beitreten.',
'WELCOME': 'Willkommen'
},
'BUTTON': {
'SUBSCRIBE': 'Abonnieren'
}
});
$translateProvider.preferredLanguage('en');
});
Code language: PHP (php)Controls

API allows us to detect current language that is in use and change language with one function — $translate.use(). Without parameters, it returns current name of translation (in our case “en” or “de”.
Simple AngularJS controller:
angular.module('myApp').controller('LangControls', LangControls);
function LangControls($translate ) {
var vm = this;
vm.changeLanguage = changeLanguage;
vm.currentLang = $translate.use();
function changeLanguage(langKey) {
$translate.use(langKey);
vm.currentLang = $translate.use();
}
}
Code language: PHP (php)Markup:
<div ng-controller="LangControls as langControls">
<button translate="English"
ng-click="langControls.changeLanguage('en')"></button>
<button translate="Deutsch"
ng-click="langControls.changeLanguage('de')"></button>
</div>
Code language: HTML, XML (xml)English and Deutsch you can not add in mapping languages file. But it is better to write it in translate directive but not in plain text.
Save chosen language
If the view in which consist application will reload language will be set to default. It is possible to save chosen language in local storage or cache.
Install angular-cookies and angular-translate-storage-cookie.
<script src="angular-cookies.js"></script>
<script src="angular-translate-storage-cookie.js"></script>
Code language: HTML, XML (xml)Add to .config of the Angular application $translateProvider.useCookieStorage();
$translateProvider.useCookieStorage();
Code language: PHP (php)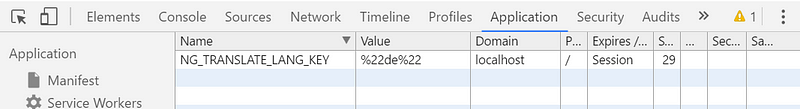
Language will be saved ing NG_TRASLATE_LANG_KEY key in Cookies.
Detect language automatically
It is possible to take navigator.language and match it with names of the translation table.
$translateProvider.registerAvailableLanguageKeys(['en', 'de'], {
'en_*': 'en',
'de_*': 'de',
'*': 'en'
}).determinePreferredLanguage();
Code language: PHP (php)The last asterisk just defines language that will be chosen if none match.
Summary
All main problems of multilingual web-sitecan be solved with existing modules. In this article, we build a simple application using angular-translate that is developed by Pascal Precht.
The result source code for this article you can find on GitHub.