SEO & AI search optimization best practices in 2026 have moved beyond keyword stuffing and mass link building, focusing instead on a cohesive, end-to-end marketing strategy that aligns with user intent and business goals.
As search engines evolve with AI, semantic search, and user-first algorithms, ranking today means understanding your audience deeply, positioning your content clearly, and distributing it smartly.
Google now rewards clarity, intent-match, and authority over hacks or shortcuts. That means SEO has evolved from a standalone marketing tactic into a foundational element of brand strategy and digital growth.
In the sections ahead, we’ll break down the fundamentals that matter most:
- Keyword research – how to target what your audience really searches for
- Technical SEO – the behind-the-scenes work that keeps your site crawlable and fast
- Content marketing – crafting pages that rank, convert, and educate
- Authority building – earning trust and backlinks the smart way
- Local SEO – getting found by nearby customers who are ready to act
Audience and Keyword Research
Keyword research is the necessary grunt work – it’s the foundation of rankings, traffic, and conversions. If it’s weak, everything else in your SEO strategy will be too.
Effective keyword research means finding terms your target audience actually searches and that you have a shot at ranking for.
Our favorite tools for keyword research are Ahrefs and Semrush. Ahrefs has deeper historical SERP data and more features for analyzing what content performs best in terms of links and shares. Semrush nails competitor analysis, showing exactly what keywords your rivals rank for and letting you drill down by URL.
What Are the Different Types of Keywords?
When building your keyword list, you’ve got plenty of options:
- Intent-driven keywords. Match the searcher’s goal, like getting extra info (“how to optimize meta tags” or purchasing a product (“SemRush pricing”).
- Long-tail keywords are more specific, lower competition, and easier to rank for queries (e.g., “best free SEO tools for beginners 2026”)
- Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) keywords are related terms that help Google understand your content’s topic. For “content audit,” think “on-page SEO,” “site structure,” or “crawl errors”.
- Comparison and modifier keywords (e.g., those with words like ‘best’, ‘2026’, ‘free’)help drive bottom-of-funnel traffic.
We’ll break down the keyword types in the next section.
How to Do Keyword Research
Here’s a step-by-step walkthrough of doing basic keyword research with Ahrefs.
Step 1: Start with a seed keyword
Head to Ahrefs Keywords Explorer. Type in a broad topic like “mobile app development”. Usually, such keywords have high search volumes, but also tough competition.
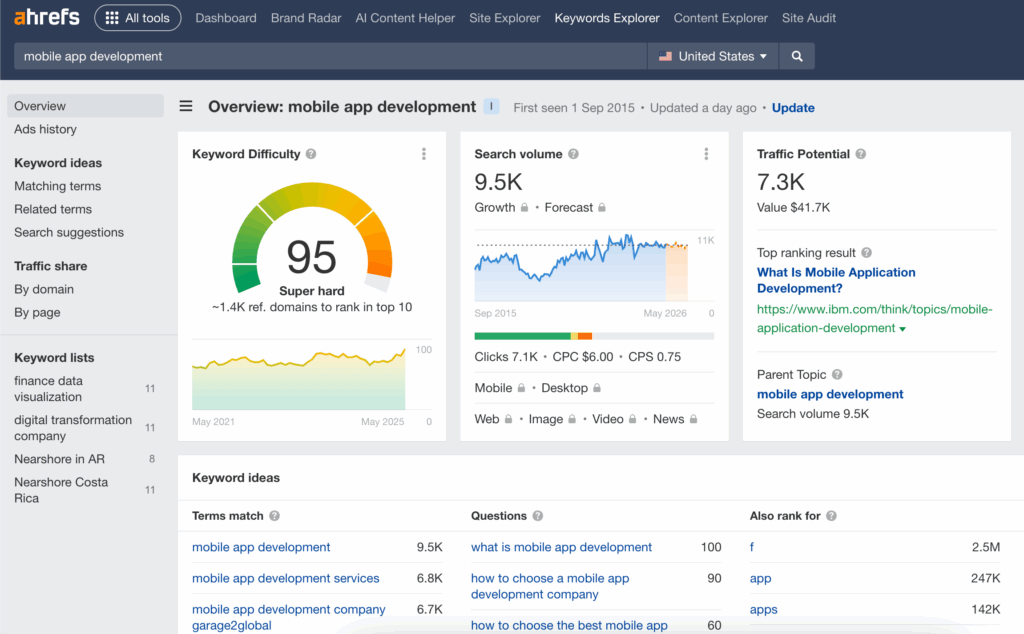
Step 2: Filter by keyword intent
Look into “Matching Terms”, “Questions”, and “Also rank for” sections to understand user intent and find more attractive keywords.
Step 3: Prioritize long-tail and low-difficulty terms
Apply filters to narrow down your list. For example:
Step 3: Prioritize long-tail and low-difficulty terms
Apply filters to narrow down your list. For example:
- Keyword Difficulty: under 30
- Volume: 100+
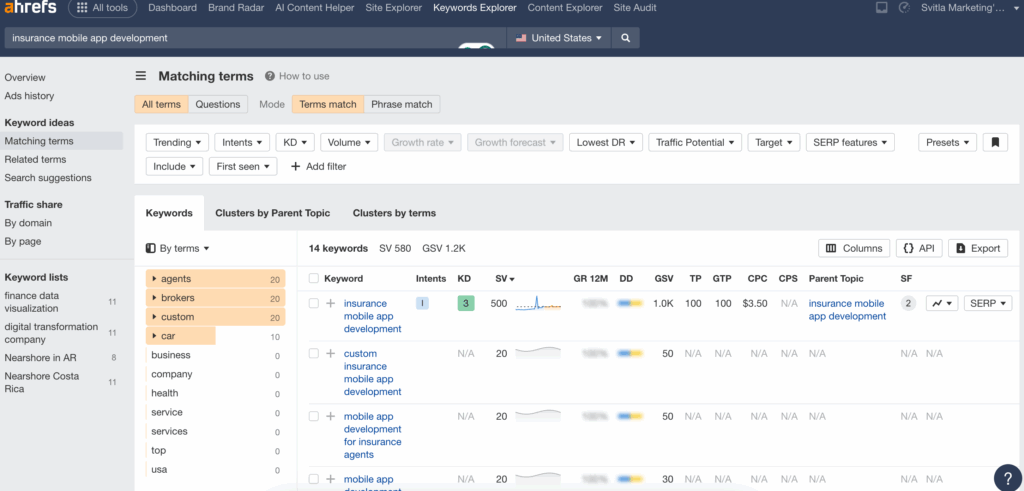
Keywords like “insurance mobile app development” or “enterprise app development” are a much sweeter target: they’re low comp, with clear intent traffic.
Step 4: Check keyword variations and questions
Browse “Also rank for” and “Search suggestions” to find keyword clusters. Copy everything in your keyword research document.
Step 5: Analyze SERP features
Paste your top keywords in Google search to see what kind of results dominate the first page:
Are there featured snippets? Videos? People Also Ask boxes? Jot that down for further content optimization.
Step 6: Build keyword clusters
Group related keywords together into themes to form content hubs – this boosts topical authority and internal linking potential.
Step 7: Export and prioritize
Export the list to a spreadsheet. Prioritize by:
- Intent fit
- Ranking difficulty
- Business value (Will this traffic actually convert?)
- SERP competitiveness
Voilà – you now have a preliminary keyword list to inform your content strategy!
Pro tip: Don’t just look at volume. A keyword with 100 searches/month but high purchase intent can outperform a 10K vanity term any day.
Focus on User Intent
There are four broad categories of search intent:
- Informational: “how to optimize meta tags”
- Navigational: “Ahrefs support”
- Transactional: “SemRush discount code”
- Commercial: “best SEO tools”
In reality, however, most keywords have a hybrid search intent: They can contain a combination of intentions (e.g., both commercial and informational). Or they can be broad and vague, attracting users with totally different intentions.
Your job is to figure out what users really want when they type a query and tailor your content to meet that need. Do that, and you’ll boost engagement, lower bounce rates, and give Google exactly what it’s looking for.
Example of a well-matched intent:
- Keyword: “inspection drones”
- Blog post: “5 best industrial inspection drones”
Example of poorly matched intent:
- Keyword: “drones inspection services”
- Blog post: “Drone inspection: Definition, Service Types”
Mine Low-Competition Keywords From Reddit
Low-competition keywords are relevant terms with no SEO rivalry. Meaning even new websites without massive budgets can rank for them relatively easily.
Reddit is the place to find those sweet opportunities. Here’s why:
In 2024, Google deepened its partnership with Reddit, gaining real-time access to Reddit content via the platform’s Data API. This move helps Google surface Reddit posts faster in search and trains its AI tools like Gemini using authentic user conversations.
It also aligns with Google’s shift toward prioritizing real, experience-based content – the kind Reddit is known for – over polished, overly optimized pages. That’s why you’re now seeing more Reddit threads in SERPs.
But not all Reddit URLs end up ranking in the top 10, which leaves plenty of room for marketers to move in.
Look for active subreddits in your niche (e.g., r/PersonalFinance, r/Fitness). Then, plug the subreddit URL into Ahrefs’ Site Explorer and filter by “Top Pages” or “Top Keywords.”
Look for threads that rank in Google, especially ones with long-tail questions or specific pain points. These often signal unmet content needs and low-difficulty opportunities.
Bonus: The language used in sub-reddits is straight from your audience’s mouth, so you’ll get keyword ideas and content angles that resonate.
Target Comparison Keywords
Searchers use comparison keywords deep in the decision-making stage (aka bottom of the funnel). Queries like “Notion vs Evernote” or “best Ahrefs alternatives” signal that someone is weighing options and ready to convert.
These terms often have lower competition but high commercial intent, making them perfect for capturing warm leads.
To optimize for comparison keywords, create:
- Head-to-head feature breakdowns
- Product comparison charts
- Pros and cons lists
- “Best alternatives” roundup posts.
Keep your comparisons objective, useful, and packed with real insights – customer testimonials, public reviews, and social media praise. Blatant bashing isn’t just bad business, it can also get you in serious trouble.
Google can put manual or algorithmic penalties on websites that make misleading representations about products or services, fabricate data, or impersonate competitors. Moreover, you can be sued under fair competition laws in many jurisdictions.
To find comparison keywords, plug your seed keyword into Ahrefs or Semrush and add modifiers like “vs,” “alternative,” or “best [X] for [Y].” You can also scan Google’s autocomplete and “People Also Ask” for extra combinations.
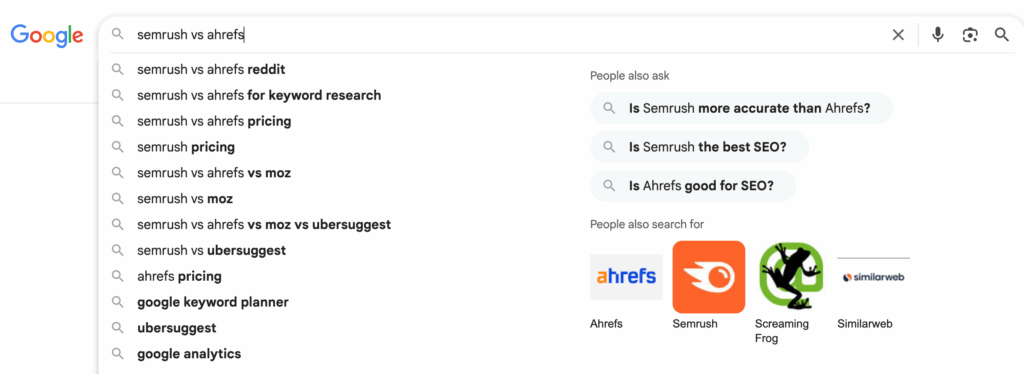
Analyze Competitor Strategies
Competitor research isn’t copying another company’s SEO playbook. In this case, you’ll always be a step behind, not ahead.
Effective competitor analysis focuses on finding content gaps, spotting missed keyword opportunities, and outdoing what’s already ranking.
With tools like Ahrefs or Semrush, here’s what you can identify:
- Top-performing keywords
- High-traffic pages
- Backlink profiles and referring domains
- Content formats that perform well
- Keyword gaps between you and them
- Anchor text patterns and linking strategies
Once you’ve got the data, reverse-engineer their success. Create content that goes deeper, answers search intent better, or formats smarter. Target keywords they’ve overlooked or under-optimized. Reach out to sites linking to their weaker content with a stronger, more relevant alternative. The goal isn’t to follow – it’s to outdo.
Technical SEO
Technical SEO deals with everything “under the hood” that helps search engines crawl, index, and rank your site smoothly. This includes:
- Website architecture
- URL structure and hierarchy
- Site speed
- Mobile-friendliness
- Site security
- Schema markup
- Canonical tags
- And more
Without getting the technical part right, you risk leaving rankings (and revenue) on the table. So be sure to apply the next technical SEO strategies.
Perform a Website Audit
Before you go SEO-galore, you need to understand your site’s health. Technical issues, broken links, slow-loading pages, and missing metadata quietly kill your rankings and user experience. We use:
- Google Search Console (GSC) to identify indexing issues, monitor Core Web Vitals, and track keyword performance.
- Google Analytics 4 (GA4) to monitor bounce rates, engagement time, and top-performing pages.
- Screaming Frog to uncover broken links, duplicate content, missing tags, and redirect chains.
Monthly technical SEO audits ensure your website is fast, well-optimized, and primed for attracting better rankings!
Essential Website Audit Checklist:
- Fix broken links – Scan for 404s and update or redirect them.
- Check crawlability – Ensure important pages aren’t blocked in robots.txt.
- Audit metadata – Review title tags and meta descriptions for length and keywords
- Test mobile usability – Ensure your site looks and works great on all devices.
- Identify duplicate content – Use tools to detect and resolve content cannibalization.
- Check indexing status – Confirm that all important pages are indexed.
- Review internal linking – Add links between related content to improve SEO and user navigation
- Optimize page speed – Compress images, enable caching, and use a CDN.
Optimize for Core Web Vitals
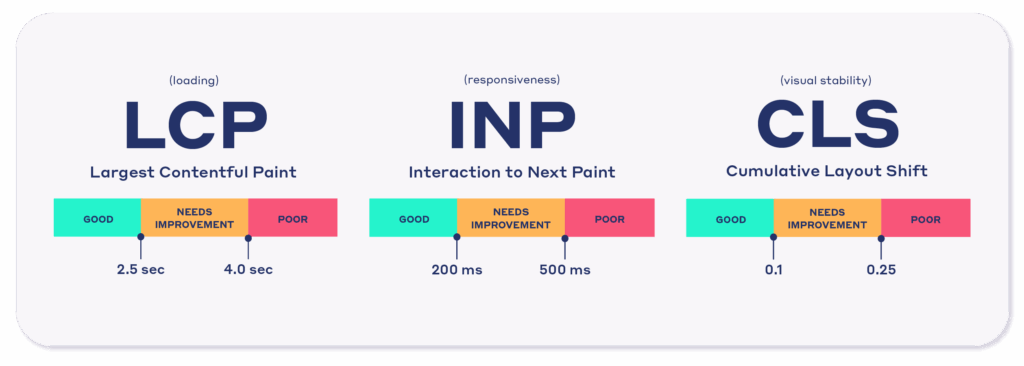
To deliver an impeccable user experience, Google created a set of compliance metrics for websites, called Core Web Vitals.
Core Web Vitals focus on three things:
- Loading speed (Largest Contentful Paint)
- Interactivity (First Input Delay)
- Visual stability (Cumulative Layout Shift).
In plain English: how fast your content shows up, how quickly users can interact, and whether the page jumps around while loading.
Improving your Core Web Vitals isn’t just about pleasing the algorithm. It’s about creating a smoother, frustration-free experience that keeps people on your site. You can check how you perform in the Core Web Vitals report on Google Search Console.
To improve your compliance, apply the following tips.
Prioritize Mobile Optimization
Google relies on mobile-first indexing, meaning it scans, indexes, and ranks websites based on the content and user experience provided by the mobile, not the desktop version.
In July 2024, Google also stopped indexing non-mobile-friendly websites. So if your desktop site is top-notch, but a mobile version is ho-hum, you’ll suffer from lower rankings.
To get mobile UX right:
- Use a responsive front-end framework that adapts layouts and interactive experiences to all screen sizes. Use file formats like WebP or AVIF for superior media compression without quality loss.
- Compress media. Use mobile-friendly image dimensions (800 x 1200 pixels for hero images and 640 x 320 pixels for blog images). Compress images to 70-80% quality on mobile and implement lazy loading to reduce page load time.
- Optimize tap targets. Buttons and links should be easy to tap without zooming. Make each about 44x44 pixels in size and keep a minimum spacing of 8 pixels between adjacent touch targets. Use relative units like em or rem for sizing to ensure tap targets scale appropriately across different screen sizes and resolutions.
- Simplify mobile navigation. Use sticky menus, collapsible sections, and large-enough CTAs to declutter the interface and improve information presentation. Place tappable elements within easy reach of the user's thumb, typically in the lower half of the screen, for better usability.
Finally, run responsive web design testing and mobile testing across devices to check performance across device types.
Improve Site Speed
Website speed is another key ranking factor. The Core Web Vitals threshold for loading speed is 2.5 seconds on mobile.
Improve Site Speed
Website speed is another key ranking factor. The Core Web Vitals threshold for loading speed is 2.5 seconds on mobile.
Anything slower increases bounce rates and hurts your rankings. A one-second delay in mobile load time can reduce conversion rates by up to 20%.
You can check your performance with the free PageSpeed Insights tool.
To boost page loading times:
- Enable browser caching. Store static files locally so returning visitors don’t have to reload them.
- Use a content delivery network (CDN). Deliver your content from servers closer to users to cut down latency.
- Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML. Strip out unnecessary characters and whitespace to speed up page load.
- Reduce third-party scripts. Excess trackers and embeds can bog down page performance.
- Lazy load offscreen content. Defer loading of images or videos until they’re needed.
Use Dynamic Parameters for Pagination
Pagination splits content across multiple pages, typically used for blogs or e-commerce product listings.
If you mess it up, you risk wasting crawl budget or creating duplicate content issues – both bad news for SEO. Google is smart enough to crawl paginated series, but you still need clean, consistent URL structures to help it understand how your website pages connect.
Good pagination structure:
- example.com/blog?page=1
- example.com/blog?page=2
- example.com/blog?page=3
Keep all versions crawlable, and make sure the canonical tag on each paginated page points to page 1 (or the main category page), not to itself. If you’re using rel="next" and rel="prev", know that Google no longer uses them, but they can still help with UX.
Pro tip: Avoid indexing paginated pages that offer no unique value. Use robots.txt or meta noindex carefully so you don’t accidentally block important content.
Apply Schema Markup
Schema markup is a type of structured data you add to your website’s HTML to help search engines better understand your content. It doesn’t change how your site looks to users, but it does change how your pages appear in SERPs.
Common types of schema:
- Article – For blog posts and news content
- Product – For e-commerce listings with price, reviews, and availability
- FAQ – For question-and-answer content
- Recipe – With prep time, ingredients, and ratings
- Event – With dates, locations, and ticket info
- Local Business – With address, hours, and contact info
- Review – To show star ratings in search
Using schema can unlock rich snippets like star ratings, images, pricing, and more, boosting your SERP visibility and click-through rates.
You can easily add schema markup to your website with Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper or WordPress plugins like Yoast SEO or Rank Math.
You can easily add schema markup to your website with Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper or WordPress plugins like Yoast SEO or Rank Math.
Content Optimization
Technical SEO lays the foundation like a solid midfield pass, but it’s content optimization that drives the ball into the net. Without both, you don’t score.
Done right, well-optimized content increases your chances of appearing in SERP features like snippets, “People Also Ask,” and image results, meaning more traffic and potential leads!
Optimize Your Content For Keyword Relevance
To rank in 2026, your content needs context, not just aimless keyword stuffing. That’s where LSI keywords and semantic terms come in.
Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) keywords and semantic terms are words and phrases closely related to your main keyword. Think “content strategy,” “SERP features,” or “backlink building” when your main topic is “SEO.” They help search engines understand the full context of your content and rank it accordingly for multiple terms.
LSI keywords are ultra important because Google’s algorithm uses natural language processing (NLP) to interpret meaning, not just match phrases. In fact, Google’s BERT and RankBrain updates rely heavily on semantic relationships to deliver better results, helping pages rank even when exact-match keywords aren't used.
“Neural matching helps us understand fuzzier representations of concepts in queries and pages, and match them to one another. It looks at an entire query or page rather than just keywords, developing a better understanding of the underlying concepts represented in them” – Pandu Nayak, Vice President of Search
To make a list of LSI keywords for your main keyword, browse:
- Google Autocomplete and “People Also Ask”
- Related Searches at the bottom of SERP results
Or you can also use tools like LSIGraph, Clearscope, or Semrush’s Keyword Magic Tool to automate the process.
When creating content, include LSI keywords naturally in subheads, introduction, image alt text, meta description, and anchors for internal links.
Always Add Meta Tags
Each content page needs a pair of unique meta tags:
- Meta title tag: A 60-character max one-liner with your target keyword near the front
- Meta description: A 155-character max teaser that includes your keyword and piques user interest.
Meta tags do a double job of communicating page content to the search crawlers – essential for indexing + rankings – and driving user clicks from SERPs.
Embed Original Images In Your Content
Original visuals aren’t just eye candy – they’re a major traffic source. Image results in Google Search see an average CTR between 1.4% and 4.9%, meaning your visuals can drive a meaningful slice of warm prospects, especially for content in visual-heavy niches like e-commerce, travel, or how-to guides.
That is, if you use original images over stock photos, which hardly ever show up in Google Image Search and blended SERP features.
Types of original images you can create:
- Step-by-step process visuals
- Data visualizations and charts
- Annotated screenshots
- Product mockups or demos
- Custom infographics
- Conceptual illustrations or diagrams
- Before-and-after comparisons
- Branded quote cards or tip cards
- UI/UX walkthroughs (for software or tools)
Bonus tip: Add GIFs
Animated images and short Reels help explain concepts quickly, break up text-heavy pages, and keep users engaged longer. Whether it’s a simple explainer animation or a looping demo of your product, motion-driven visuals create visual anchors that pull users deeper into your content and keep them scrolling.
You can also repurpose animations for social media for effective cross-promotion and audience building.
Optimize for Featured Snippets
A featured snippet is the boxed answer Google shows at the top of some search results (aka position zero). It pulls a short, direct answer from a web page and links back to it, giving you massive visibility and click-through rates up to 44%.
Common snippet formats include:
- Paragraphs (definitions or quick answers)
- Numbered or bulleted lists (steps, rankings)
- Tables (comparisons, data)
- Videos (how-tos or explainer clips)
To win featured snippet results, you need to:
- Optimize for long-tail, question-styled queries
- Answer the question clearly and directly in the first 40–60 words
- Use H2 or H3 headers to break up sections
- Format step-by-step processes as numbered lists
- For comparisons or stats, use clean HTML tables
- Include the target question in the subheading (e.g., “What is a featured snippet?”)
Keep your content scannable, specific, and structured – that’s what Google loves to pull.
Build Out Content Hubs
A content hub is a central pillar page linked to multiple related sub-pages – a structure known as a topic cluster. Think of it as your SEO command center: one high-authority page covering a broad topic, supported by in-depth articles targeting related long-tail keywords.
Content hubs help Google understand the depth of your expertise, improve internal linking, and spread link equity across related pages – all of which boost rankings. They also keep users engaged longer by guiding them through logically connected content.
How to build a content hub
Start with a core topic (e.g., “SEO Strategy”), built around your main, high-volume, and high-competition target keyword. Then create subtopic pages like “Keyword Research,” “Technical SEO,” “Content Optimization,” etc, based on relevant lower competition terms.
Link each cluster page back to the main hub and to each other, where relevant. Use consistent anchor text and clean URL structures to streamline user navigation and promote longer on-site sessions.
Diversify with Seasonal Content
An effective SEO strategy is about 80% evergreen content and 20% seasonal or timely pieces. That 20%? It’s your chance to ride the wave of trending searches, target lower-competition keywords, and get quick wins that boost visibility and grow traffic. Think timely topics tied to events, holidays, industry news, or yearly updates.
Examples of seasonal/timely content formats:
- “Best [Industry Tool] for [Year]”
- “Holiday Marketing Tips for [This Season]”
- “Q4 SEO Checklist for [Year]”
- “Trends to Watch in [Year]”
- “How to [achieve result] before [Holiday]”
- “What [Industry Change] Means for Your Business”
Seasonal content positions you as current and relevant, earns backlinks from sites looking for fresh sources, and helps you appear in time-sensitive search results.
Bonus: You can repurpose and update it annually to build compounding traffic over time.
Optimization for AI-Powered Search
AI assistants now sit between your buyer and your website. People increasingly ask ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overview for options, trade-offs, and next steps before they ever land on a SERP. Recent polling shows that about 60% of U.S. adults, and roughly three-quarters of people under 30, use AI tools to search for information at least some of the time.
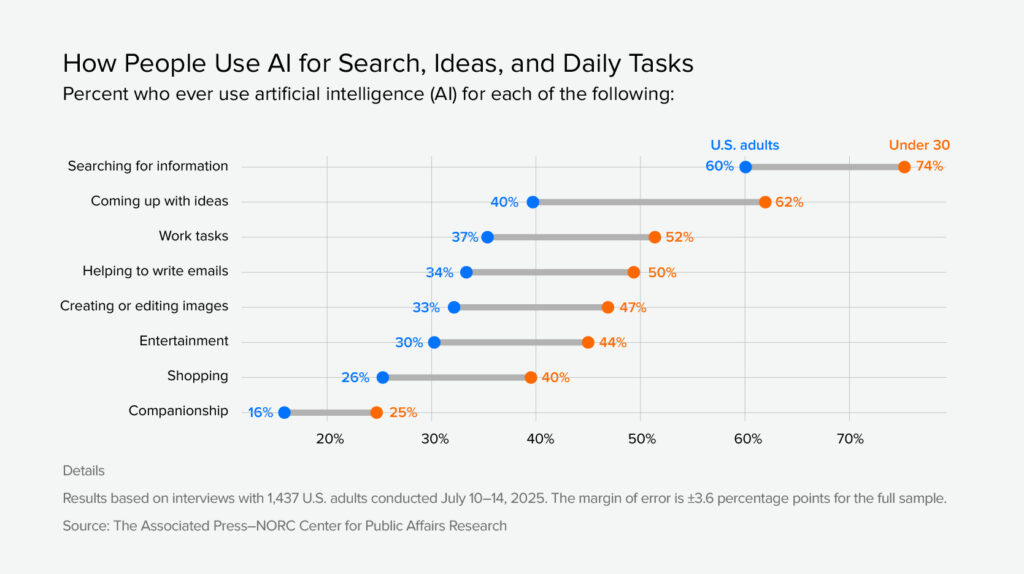
Google is still the main traffic driver, but assistants are becoming a fast-growing source of high-intent visits and brand mentions. If your pages aren’t easy for them to find, parse, and quote, you risk disappearing from that early “advisor” stage of the journey.
Assistants pull answers from search indexes and high-authority platforms. They lean on Bing and Google to discover pages and then cross-check sources like YouTube, Wikipedia, Reddit, GitHub, Stack Overflow, G2, Capterra, and trusted niche media. Clear, structured pages, FAQs, comparisons, how-tos, specs, and tables,make it easier for LLMs to summarize your content and attribute it properly.
Think of AI assistants as personal consultants. They weigh options, explain trade-offs, and suggest what to do next. Your brand should appear in that advice, either as a cited source or as a recommended vendor.
Practical ways to adapt your SEO to LLMs
Align content with assistant-led research
Keep your classic SEO workflow, but plan content as if a bot will read, summarize, and recommend it to your buyer.
- Map the full journey with task-based pages: short explainers and “how it works” pieces for awareness; “X vs Y,” implementation playbooks, ROI explainers, and procurement guides for consideration; pricing notes, integration pages, and case studies for decision; admin guides and success plans for post-purchase.
- Lead with the answer, then outline steps, pitfalls, and a copy-ready asset (checklist, calculator, or template) that assistants can surface directly.
- Target long, precise prompts that match real questions, such as:
- “Which SOC 2-ready log tool integrates with BigQuery, supports EU data residency, and stays under $1K/month?”
- “Nearshore data-engineering partners in Eastern Europe with healthcare (FHIR) experience and ISO 27001.”
These queries look very close to what users type into assistants and tend to show up in LLM answers.
Fix findability and crawl access for AI bots
Assistants assemble answers from search indexes and high-authority sites, so crawlability still comes first.
- Keep key pages within three clicks, maintain valid XML sitemaps and stable URLs, and fix broken links before new content sprints.
- Treat AI user-agents as another channel. Make sure robots.txt and your CDN/firewall rules are not blocking reputable AI crawlers like GPTBot or Perplexity’s crawler if you want them to access your content.
- Log AI user-agents and IP ranges, watch for 403/429 spikes, and keep Core Web Vitals healthy so both users and bots can render your pages cleanly.
Turn priority pages into quotable sources
Assistants favor content that is easy to synthesize and safe to quote
- Use short paragraphs, explicit headings, and direct, two-sentence answers at the top of each section. Then add steps, trade-offs, and examples.
- Add compact FAQ blocks that mirror the way people actually ask questions.
- Include small, trustworthy numbers (benchmarks, ranges, before/after deltas) and show a visible “last updated” date to reinforce freshness.
- Add copy-ready elements like comparison tables, short checklists, and configuration examples that assistants can lift into AI Overviews and answer cards.
Studies show that pages which already rank organically are more likely to be cited in AI Overviews and similar features, so solid SEO and clear structure now work together instead of in isolation.
Build off-site proof that assistants can verify
LLMs cross-check your authority across the open web, not just on your domain
- Treat review ecosystems and reputable third-party directories (e.g., G2, Capterra) as primary trust signals. Maintain accurate profiles, verified reviews with concrete use cases, and clear pricing context.
- Keep clean entries on platforms like Crunchbase or Wikipedia where relevant, contribute expert quotes to niche media, and add helpful posts to communities such as Reddit, Stack Overflow, or industry-specific forums.
- Short YouTube explainers and demo clips also feed LLM answers because they combine authority with clarity.
A quick readiness checklist
Use this as a simple LLM-SEO health check before scaling content further:
- Can reputable AI crawlers access and render your key pages?
- Do your cornerstone pages answer real tasks in plain language, with clear examples and a next step?
- Do you have at least one credible third-party mention and several verified reviews in the ecosystems your buyers trust?
- Are assistant referrals (chat.openai.com, gemini.google.com, perplexity.ai, etc.) tracked as a separate channel in your analytics, instead of being excluded as “spam” or grouped under direct?
If the answer is “no” to most of these, fix them first. Then keep doing what strong SEO has always required: fast pages, clear architecture, user-first content, and consistent proof that real people trust your brand. The difference in 2025 is that you’re optimizing for both human readers and the AI assistants that advise them.
Link Building and Authority Building
Link building isn’t just about racking up (paid) backlinks anymore – it’s about building authority. Google algorithms are great at distinguishing genuine, relevant mentions from reputable sources from low-quality links from some shady websites.
So the paradigm has shifted from chasing links in bulk to selectively acquiring them
by creating content people want to cite, share, and talk about. Modern link building is strategic, relationship-driven, and focused on long-term credibility, and this is how we recommend executing it.
Focus on E-E-A-T
E-E-A-T (or "Double-E-A-T") is Google’s framework for assessing content quality, especially in YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) niches like health, finance, and legal. It’s part of its Search Quality Rater Guidelines for human reviewers, who assess the quality of search results.
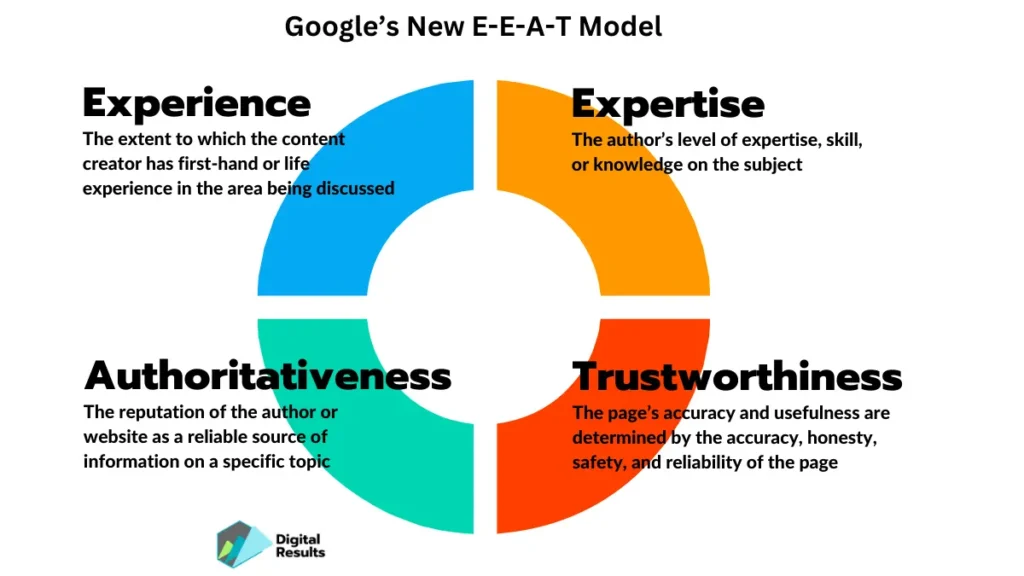
Google wants to show users content that’s credible, accurate, and created by people who know what they’re talking about. Thin, anonymous, or unverified content? It gets buried deep in search results.
That’s because Google wants to display results from content creators who have first-hand experience with the subject they’re talking about.
Here’s how to demonstrate strong E-E-A-T:
- Include author bios with a list of their credentials (e.g., work title, professional affiliations, certifications), along with social profiles (e.g., Twitter, LinkedIn) to demonstrate their expertise.
- Cite sources and fact-check. Link back all important claims to original, reputable sources. Disclose information collection methods (e.g., if you ran a survey or did some data analysis). Verify all statements for accuracy and recency.
- Curate real reviews and testimonials. Display ‘social proof’ from your customers through featured endorsements or embedded social media shoutouts. Include these as direct, linked quotes to showcase that these come from real people, not bots.
- Display trust signals. Ensure your website covers all the basics like a secure HTTPS connection, clear privacy policies, contact info, and ample company information, explaining who you are and how you operate.
- Get mentioned on trusted sites. Backlinks from reputable media sources – industry blogs, news outlets, government or .edu domains – signal to Google that your site is credible. You don’t need hundreds of backlinks – a few from authoritative sources go a long way.
To succeed with SEO in 2026, you need to build credibility for your brand, not just acquire links en masse. And here’s how to do this:
Plan an Outreach Campaign
Backlinks from high-authority sites remain one of the strongest ranking signals in 2026, but you need to work for them. A strategic outreach campaign puts your content in front of the right people to earn those links.
Start by identifying websites in your niche with solid domain authority (use tools like Ahrefs or Moz). You can also analyze your competitors' backlink profiles to identify link opportunities you can replicate or improve.
Then try different strategies for or link acquisition:
- Offer linkable assets. Instead of sending cookie-cutter outreach emails, offer something worth linking to – original research, expert insights, custom visuals, or a fresh take on a trending topic. Suggest your content as a useful resource or contribute guest posts with real value.
- Leverage digital PR. React quickly to news in your space by offering expert quotes or timely data. Many journalists publish source requests on LinkedIn. Or you can respond to requests on specialized platforms like Qwoted, SourceBottle, and Help a B2B Writer.
- Get listed in roundups. Pitch content to weekly newsletters or curated roundups in your industry. These often drive targeted traffic and earn passive backlinks over time.
- Partner up with nonprofits and educators. Create special discounts or unique resources for students, educators, or nonprofits. Such resources often get linked from .edu or .org domains – pure gold for domain authority.
Remember: Outreach is a marathon. Reach out across multiple channels: email, LinkedIn, Twitter DMs, or even contact forms – and follow up once.
Build Backlinks With Podcasts
Appearing as a guest on industry-relevant podcasts is a low-effort, high-reward way to earn backlinks. Hosts almost always link to your website, social profiles, or resources in the show notes. Podcasts also position you as a thought leader (think extra E-E-A-T points!) and give you content you can repurpose (transcripts, clips, quotes).
Research podcasts in your niche via Listen Notes. Then reach out to hosts with a quick intro email. Pitch your bio, a few topic ideas, and links to past interviews or content. Focus on offering unique insights or stories, not self-promotion, to score an appearance.
Enter a Content Alliance
A content alliance is a smart way to gain backlinks, visibility, and credibility through content co-creation with another brand in your niche. Each partner promotes the content, links to it, and shares it with their audience, multiplying reach and backlink potential.
Co-branding initiatives work best when both parties bring something to the table: one might have data, the other distribution. Choose partners with aligned (but not competing) audiences, and set clear goals up front. Publish on one site or create a neutral landing page, just make sure both sides link back.
Ideas for co-branding campaigns:
- Joint industry report. Partner on original research or surveys, publish findings as a branded whitepaper.
- Webinar or Live AMA. Co-host an educational or Q&A session and cross-promote to both audiences.
- Co-branded e-book or guide. Create a downloadable resource combining expertise from both sides.
- Linked blog series. Publish companion blog posts on each brand’s site that interlink and share insights from different angles.
- Podcast guest swap. Feature each other on your respective podcasts or create a limited co-hosted mini-series.
- Case study collaboration. Showcase a joint success story or customer transformation powered by both brands.
- Newsletter cross-promotion. Curate each other’s content, tools, or offers in your email newsletters to tap into new, relevant audiences and drive high-intent traffic.
Get Backlinks From Unlinked Brand Mentions
If people are already talking about your brand, you’ve got backlink opportunities just waiting to be claimed. In fact, 77% of brand mentions go unlinked!
Use tools like BuzzSumo, Ahrefs Content Explorer, or Google Alerts to find unlinked brand mentions – articles or blog posts that mention your company, product, or team but don’t link back to your site.
Once you find a mention, reach out to the author with a quick, polite email. Thank them for the mention and suggest adding a link to your homepage or a relevant resource. Keep it low-pressure and make it easy for them.
Why it works: the hard part (getting mentioned) is already done. Now you’re just connecting the dots – and earning high-authority backlinks in the process.
Optimize for “Journalist Keywords”
Journalist keywords are the search terms reporters use when hunting for expert quotes, stats, or quick explanations. Think “healthcare technology trends 2026,” “AI adoption statistics,” or “new startups in FinTech”.
Targeting these keywords puts your content in front of the right people at the right time, increasing your chances of earning organic citations and high-authority backlinks from media outlets on autopilot.
How to do it:
Create data-driven content like original research, trend roundups, and explainers.
Use clear H1s like “What is [Topic]?” and include quotable insights or stats. Structure content so it’s easy to skim and reference – journalists don’t have time for fluff. Free tools like Exploding Topics and Google Trends can help you spot rising topics worth targeting.
When done right, journalist keywords turn your content into a backlink magnet without cold emails or outreach.
Local SEO
Local SEO is essential for any business that targets niche geo-audiences – from coffee shops to law firms. Over 1.5 billion monthly searches have a “near me” modifier, and 28% of them lead to a purchase. If you're not optimizing for those queries, you’re missing high-converting traffic.
Ranking in the local pack means more visibility on Google Maps, better mobile presence, and a direct path to phone calls, foot traffic, and sales. With zero-click searches rising, having an optimized Google Business Profile, local citations, and positive reviews also helps you stay visible and competitive.
Optimize Your Google Business Profile
Your Google Business Profile (formerly Google My Business) is your local SEO powerhouse. It’s what shows up in local packs, Maps, and “near me” searches, so optimizing it is a must.
Here’s what to do:
- Claim and verify your listing using your official business account. Give a real mailing address because Google will send a physical letter.
- Use your exact business name. Don’t sneak extra keywords – you’ll get penalized for that.
- Choose the most accurate category. Add secondary ones if relevant, but don’t go beyond three different ones.
- Write a keyword-rich business description that clearly explains what you do. Mention your key services and value proposition.
- Upload high-quality photos of your location, team, and products – visual trust matters.
- Add accurate hours, phone number, pricing, and website. Keep the info updated to avoid customer frustration.
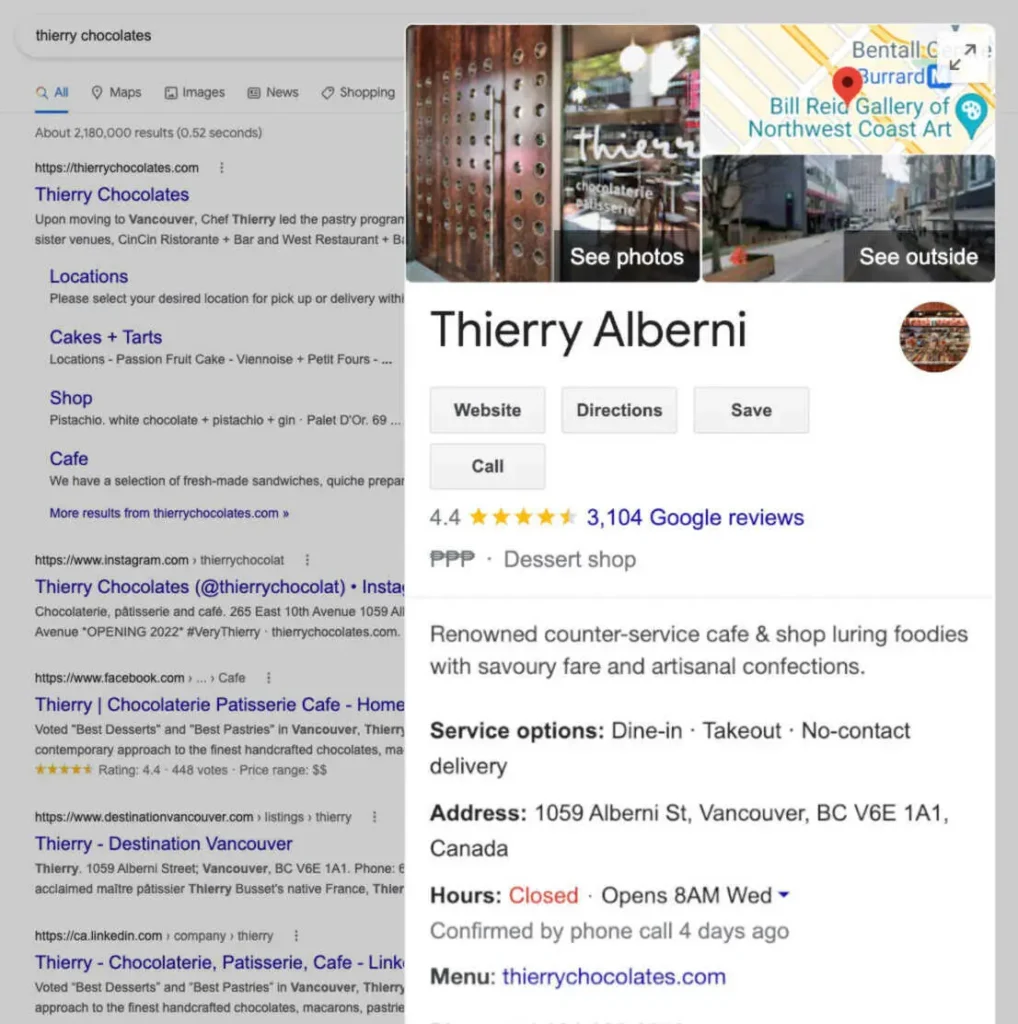
Target Local Keywords
Local keywords are search terms that include a specific location, like “pizza delivery in Paris” or “best bookstore near Times Square.”
They help your business show up in local search results where intent to visit or buy is high. To find them, use tools like Google Keyword Planner, Semrush, or simply look at autocomplete suggestions and "People Also Ask" in your region.
To optimize for local terms:
- Include city or neighborhood names in titles, H1s, and meta descriptions
- Add localized keywords naturally into page copy, especially service and location pages
- Create individual landing pages for each service area or location to target searchers in different regions
- Use schema markup to define your business’s geographic presence and add extra features like pricing, reviews, etc.
- Display your address and local phone number in the site footer
Solicit Customer Reviews
Customer reviews are a key trust signal for both users and search engines.
According to a BrightLocal study, 74% of consumers read at least two local reviews online, and 89% expect businesses to respond to all types of reviews (including criticism!). Sterling Star Inc., in turn, determined that local businesses with 10+ 5-star reviews on their Google Business Profile get a ranking boost.
To collect more Google reviews:
- Ask at the right time. Request a review after a successful service or upon order delivery. When people are content, they’re more likely to engage.
- Make it easy. Send a direct link to your Google review page via email, text, or post-purchase follow-ups. Place a QR code near the cash register or around the premises at your location.
- Give an extra incentive. Offer a “sweet something” for reviewing your business – a small discount for an extra purchase or a complementary product.
More reviews = more trust = more visibility. So, make review collection part of your ongoing local SEO strategy.
Build Local Citations
Local citations – mentions of your business name, address, and phone number (NAP) on directories – help Google verify your legitimacy and boost your local search presence. Consistent listings across platforms like Yelp, Yellow Pages, Apple Maps, and industry-specific sites improve trust and visibility in the local pack.
Tips to find citation opportunities:
- Start with core directories like Google Business Profile, Bing Places, Yelp, and Facebook
- Use tools like Moz Local, BrightLocal, or Whitespark to discover niche and geo-specific directories
- Google your competitors’ business names to see where they’re listed – then submit your info there too
- Check for accuracy and duplicate listings. Even small inconsistencies can confuse search engines and diminish the returns.
Local SEO is built on trust and consistency, and citations are the digital breadcrumbs that lead customers (and Google) straight to you.
Conclusion
The rules of SEO have changed. Ranking in 2026 means aligning content with user intent, optimizing every technical detail, and earning trust through authority, accuracy, and real expertise.
SEO is no longer about gaming the system. The goal is to deliver the best content and user experiences across search, AI tools, and local discovery.
Svitla Systems offers full-cycle SEO setup and ongoing optimization as part of our Marketing Support Services. From keyword research and technical audits to content creation and authority building, we’ll help you implement a future-proof SEO strategy that delivers consistent ROI. Let’s talk about how Svitla can support your growth.

![[Blog cover] SEO optimization best practices](https://svitla.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/Blog-cover-SEO-optimization-best-practices-936x527.jpg)
![[Blog cover] SEO optimization best practices](https://svitla.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Nataliia-Romanenko-236x236.jpg)


