Modern client-server systems
Nowadays modern client-server systems are very popular and this trend has been observed for about the last 30 years. With the development of data communication channels and Internet protocols and an increase of speed and quality (stability) of data transmission, the model of building distributed or interconnected components is reasonably included in the architecture of information systems. The simplest concept of a distributed system is based on the exchange of data between the client and the server. With the development of HTTP protocols, this model has become the most widespread and most of the modern Internet works on this foundation. Once such an architecture is working, the question of agreements and standards for the transfer of information between the client and the server naturally arises.
One of the oldest protocols for data exchange is Remote Procedure Call or RPC. The first systems of distributed computation based on the RPC concept were put in place in the late 1960s. RPC was based on the request-response protocol. This method came into use as a basic and fundamental organizing principle. However, RPC is difficult in a heterogeneous environment since it requires Interface Description Language (IDL) for various platforms and is often difficult to implement and support.
SOAP protocol was created in late 1990 representing the next generation of the request-response concept. SOAP defined message protocol specifications for information exchange between client and server. It gives more flexibility and simple usage within heterogeneous systems, independent from programming languages.
Learning from SOAP’s advantages and disadvantages, the next generation of protocols promoted the bright idea of the “state-less” concept. The simplicity and power of Representation State Transfer (REST) architectural style allowed building reliable, fast, and effective request-response client-server systems starting in the early 2000s.
Another important factor in the development of modern client-server systems was the use of the JSON format for describing the transmitted data. JSON is simpler and more compact than XML and allows building lightweight parsers on the client side.
Let’s find the difference between Soap vs Rest vs Json in the details.
What is SOAP?
SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) is the Messaging Protocol layer for web services. It is an XML-based protocol for information exchange between client and server using the request-response communication model. SOAP can work over both SMTP protocol and HTTP protocol. In the Open Systems Interconnection model (OSI) SOAP takes a high-level place in the hierarchy.
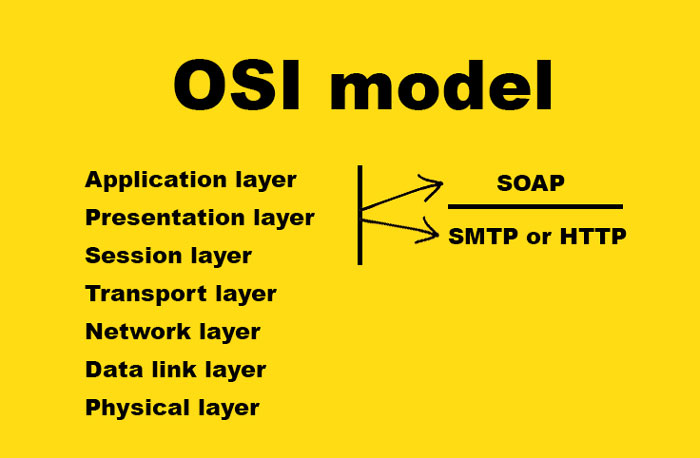
On the presentation layer, SOAP uses XML to encode and represent information. This protocol is independent of operating systems and programming languages.
SOAP has four main building blocks which are:
- Envelope element to identify the XML as a SOAP message
- Header element
- Body element that contains request and response information
- Fault element to describe status and errors
The structure of a SOAP message is shown in Fig. 2. In the client-server model, it allows encapsulating various data types. The concept of message sender and receiver in SOAP following roles: SOAP sender, SOAP receiver, SOAP message path, SOAP intermediary, Initial SOAP sender, and Ultimate SOAP receiver. The combination of these roles allows architects and developers to build complex and effective interconnections in systems.
A specification of SOAP describes processing and extensibility models, underlying protocol binding, and the structure of a SOAP message. This avoids connection confusion when different systems from separate companies are involved.
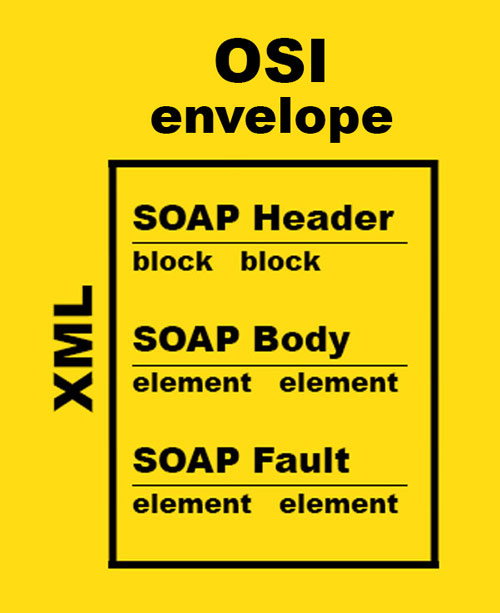
From this page you can find an example of SOAP envelope, header, etc:
POST /InStock HTTP/1.1
Host: www.example.org
Content-Type: application/soap+xml; charset=utf-8
Content-Length: nnn
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<soap:Envelope
xmlns:soap="http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap-envelope/"
soap:encodingStyle="http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap-encoding">
<soap:Body xmlns:m="http://www.example.org/stock">
<m:GetStockPrice>
<m:StockName>IBM</m:StockName>
</m:GetStockPrice>
</soap:Body>
</soap:Envelope>
Code language: HTML, XML (xml)What is REST API?
REST is a software architectural style for web services. Actually, it is not a protocol itself, but a set of rules or guidelines for building an effective communication model between sender and receiver of information. RESTful Web services are built with a list of constraints that simplify client-server information exchange and their software implementation.
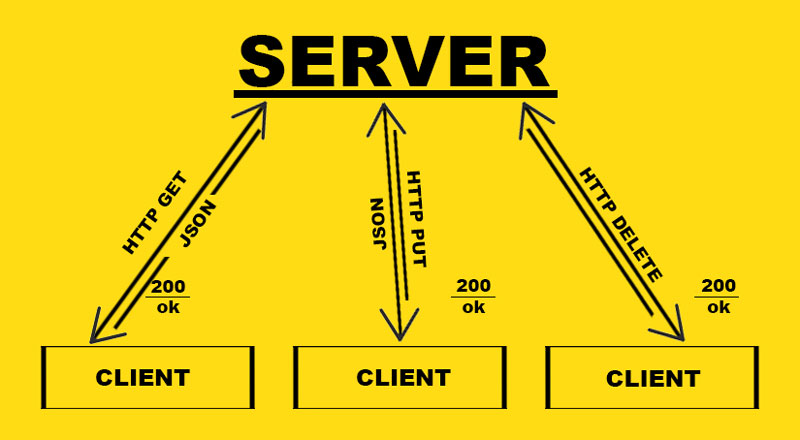
REST API works over HTTP protocol. It has the same place in the OSI model as SOAP. RESTful service uses four methods from HTTP protocol: get, post, put, and delete. These methods are restricted to storing client status on the state server, i.e. “stateless”. REST API can represent data in the form of HTML, XML or as JSON (Fig. 3). The RESTful application builds logic around resources, but not around endpoints.
Representation State Transfer has the following rules or rather restrictions:
- Client-server architecture
- Statelessness (“no client context being stored on the server between requests”)
- Cacheability
- Layered system
- An optional code on demand
- Uniform interface (resource identification and manipulation, self-descriptive messages)
REST vs SOAP
Looking for the answer to the question - REST vs SOAP - you will not find a direct answer. Why? Because they are designed to solve different problems.
How to solve the problem of choosing REST vs SOAP? The answer can be very simple from one side yet very complex from another point of view. The simple answer is REST. This architectural style (but not a standard) is more popular and widely used in most modern services and web sites. REST is simpler compared to SOAP and requires fewer resources on both the server and client sides.
At the same time, REST has rather limited capabilities, in comparison with SOAP. SOAP was designed for solving different types of tasks than REST.
First of all, SOAP is a standard, but REST is a guideline for architectural style. Then, SOAP has built-in security components. SOAP can work on more Internet protocols compared to REST. On the other hand, SOAP is heavy for use on mobile platforms.
SOAP is perfect to use on distributed systems and corporate/enterprise level applications. REST is perfect for multipurpose high-performance systems with different platforms and components.
REST and SOAP are not direct (or indirect) competitors. The choice of the appropriate technology should be based on the analysis of the system and the knowledge of developers who have experience in using both REST and SOAP.
Difference between: SOAP vs REST
What is the difference between SOAP and REST? They have many similarities in the fundamentals but also differences in the details.
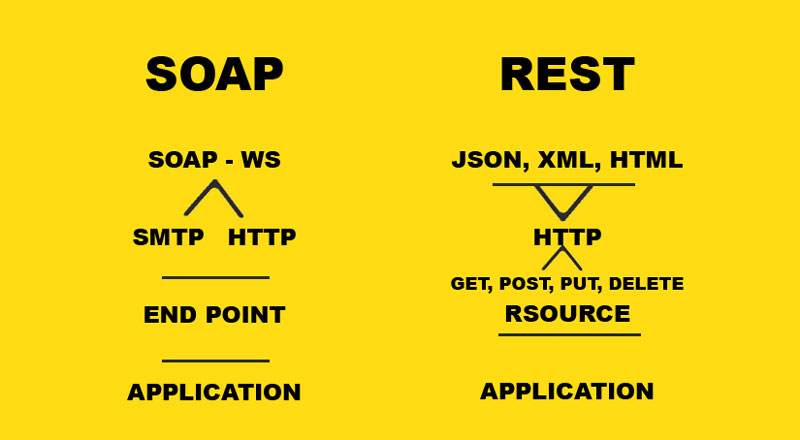
The differences are following.
SOAP
- Standardized protocol with pre-defined rules to follow.
- Data as service, function-driven.
- Calls cannot be cached.
- On presentation, layer works with XML only.
- Works well on enterprise and corporate level, high-level security applications.
- Requires too many resources.
REST
- Architectural style with no standardized description.
- Stateless (no server-side information about client state).
- A cache is available for API calls.
- On presentation layer works with JSON, XML, HTML, etc.
- Works well on the public API level, microservices, and systems with high scalability.
- Requires fewer resources.
The role of JSON and its influence
JSON is a form of information representation in text form. Fortunately, JSON is pretty well standardized as RFC 7159, “The JavaScript Object Notation”. It is so popular for coding information in text files, that it is used now not only in JavaScript but everywhere.
As an alternative to XML, JSON has a simpler structure, and parsers are available for every programming frameworks or libraries.
The Influence of JSON on modern information systems is incredible. Google, Twitter, Facebook, cloud systems, etc. work with JSON and their API is suited for this format as well as REST.
JSON supports all basic data types: number, string, boolean, array, null and object. The object type is an unordered collection of name-value pairs. The Unicode standard allows the use of any language in string elements in JSON.
JSON schema allows validating JSON format which is very useful for avoiding errors in data coding/encoding.
JSON is self-descriptive, easy to understand and simple. For example:
{"menu": {
"id": "file",
"value": "File",
"popup": {
"menuitem": [
{"value": "New", "onclick": "CreateNewDoc()"},
{"value": "Open", "onclick": "OpenDoc()"},
{"value": "Close", "onclick": "CloseDoc()"}
]
}
}}
Code language: JSON / JSON with Comments (json)In many ways, the success of REST is due to the JSON format because of its easy use on various platforms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we note that in a battle of Soap vs Rest vs Json each of them has its own advantages. The main task at the stage of the system design is the right choice of technology. This will save considerable time, resources and increase the reliability of the system. To ensure better compatibility with mobile platforms, heterogeneous systems, and ease of description in the JSON format, it is necessary and recommended to use REST. To build a corporate multi-component system with distributed endpoints and integration with heavy and powerful frameworks, we recommend using XML and SOAP. Based on various communication protocols (SMTP and HTTP), SOAP is quite flexible and robust in terms of network communication. Data representation in the form of XML has advantages for building effective systems over SOAP. At the same time, SOAP is complex and great for large systems but less effective for simple and heavy duty client-server applications.
The art of choice always lies in the plane of knowledge technology basics and practical experience. Svitla Systems has broad experience in both REST and SOAP, whether building a system from scratch or supporting and troubleshooting existing software systems.
Why Svitla?
As a tech-savvy company, we are always at the forefront of the most widely used tools and protocols, as well as cutting-edge technology. All with the purpose of serving our customers with the best possible toolset that will transform and innovate.
For more information, contact our sales team by filling out the form below.