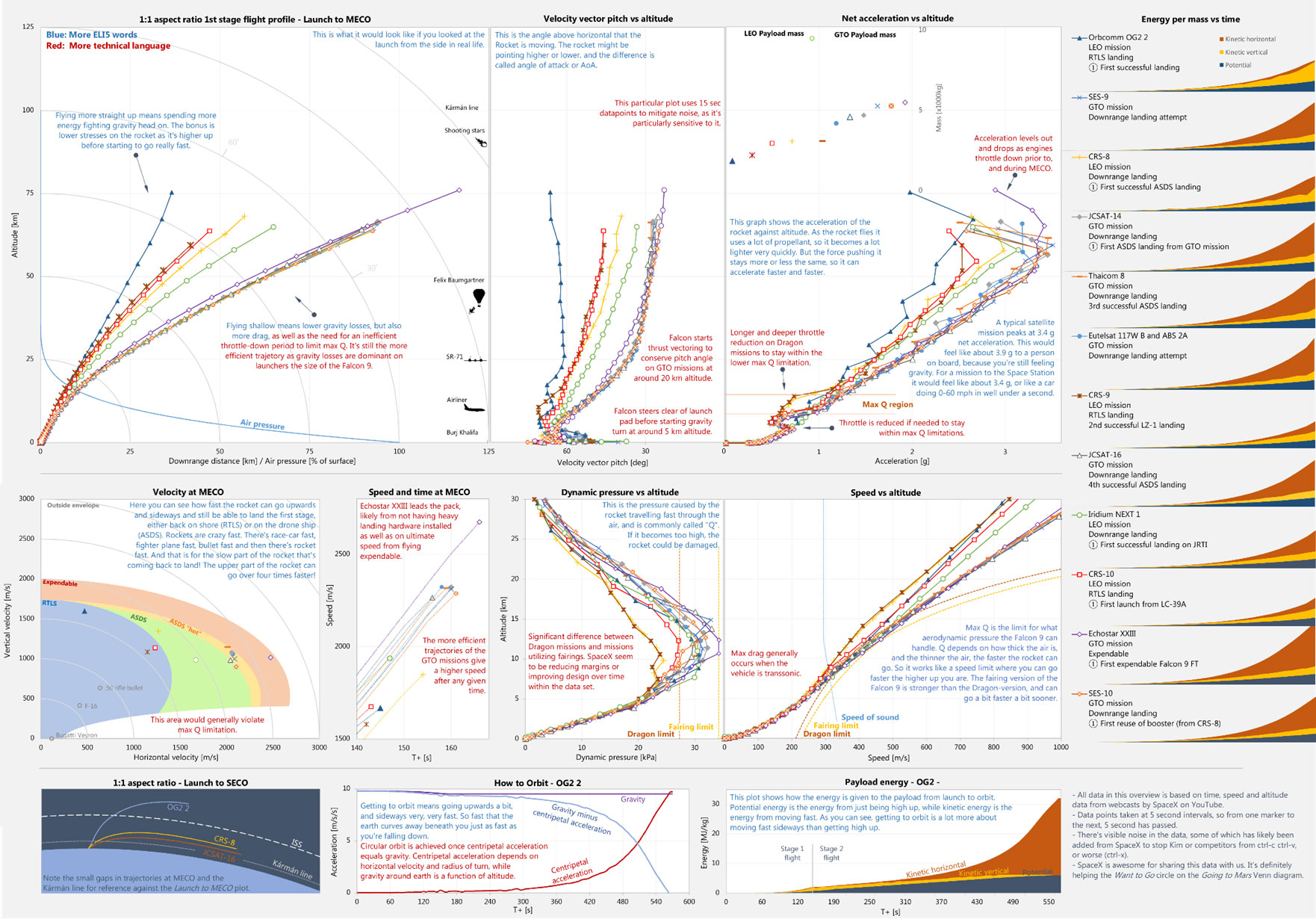
The world is creating so much data that businesses are struggling to find strong storage options. A wide range of industries, from agriculture to space research, use Big Data to make better business decisions. Managing and keeping Big Data, however, can be a difficult task. Businesses need to find a way to meet their storage needs while getting the most out of their infrastructure investments.
In this article, we look at the things businesses need to think about when figuring out how much they need to spend on storage infrastructure to handle Big Data optimally.
Unleashing the Power of Big Data: The Crucial Role of Robust Storage Applications
In the world of big data, where a lot of information is created and studied, storage is a key part of how large data sets can be processed and managed. Because of the sheer amount, speed, and variety of data involved in big data projects, companies need a strong and scalable storage infrastructure to get the data-driven insights they want. In this section, we'll cover why Big Data storage is so important and how they help organizations get the most out of their data assets.
Handling Big Data Sets
Big Data consists of a lot of structured and unstructured data from sensors, social media, transaction records, and other sources. It is necessary to store and manage Big Data sets to perform analytics and get useful insights from them. A good Big Data storage system, like a cloud storage option, has the space and scalability to handle the huge amounts of data that are being created.
Example: A cloud storage solution like Amazon S3 provides the necessary capacity and scalability to handle the vast amounts of structured and unstructured data generated by, let’s say, the latest SpaceX landing or Amazon’s Prime Day biggest sale of the year. In turn, organizations have the power to transform those large chunks of data into actionable items like customer behavior metrics for large retailers or improvement areas to send rockets to space with absolute precision.
Real-time Data Analysis
Big Data applications often need real-time or near-real-time analysis to get useful insights and make good decisions. By lowering latency and making sure that data can be retrieved quickly, storage solutions help make sure that important information is available when it is needed.
Example: With a high-performance storage solution like Google Cloud Storage, organizations can ensure low latency and fast data retrieval, facilitating real-time or near-real-time analysis of Big Data. For instance, a logistics company can use real-time data analysis capabilities to collect and analyze real-time data from GPS trackers on their fleet vehicles, thus optimizing route planning, improving delivery efficiency, and responding swiftly to unexpected events like traffic congestion or accidents. This allows them to provide better customer service, minimize delivery delays, and reduce operational costs.
Data Security and Reliability
The accuracy and security of data are some of the most important things to think about when prospecting storage solutions. Robust storage solutions have features like data encryption, access controls, and backup systems to protect data from being accessed by people who shouldn't be able to and from being lost. Also, storage systems that are reliable and have built-in redundancy and fault tolerance help protect data from hardware breakdowns and make sure it is always available.
Example: Robust storage solutions like Microsoft Azure Blob Storage offer advanced security features such as data encryption, access controls, and backup systems. For instance, a healthcare organization can prioritize data security and reliability in their storage solution to protect sensitive patient information. By storing electronic health records (EHRs) securely with encryption, access controls, and regular backups, the organization ensures the privacy and integrity of patient data. Additionally, implementing a redundant storage infrastructure and disaster recovery mechanisms safeguards against data loss, ensuring continuity of care and maintaining trust with patients.
Accessibility and Scalability
Big Data storage needs to be easy to get to so that data can be found and analyzed quickly. Modern storage technologies, especially cloud-based ones, are flexible and scalable enough to meet the needs of Big Data apps as they grow. With cloud storage, companies can increase or decrease their storage space based on their needs. This lets them avoid the limitations of on-premises infrastructure and physical storage devices.
Example: Cloud-based storage platforms such as IBM Cloud Object Storage provide easy accessibility to Big Data, allowing organizations to quickly locate and analyze the required data. For instance, a marketing agency can leverage cloud-based storage to centralize and access large marketing campaign datasets from various sources. This allows marketing analysts to quickly access the required data for campaign performance analysis, segmentation, and targeting. As the agency acquires new clients and expands its dataset, the scalable storage infrastructure ensures seamless growth without disruptions, enabling efficient data-driven decision-making and effective campaign optimization.
Big Data Storage Properties
Big Data applications process huge amounts of data, so they need storage options that can handle their specific needs. In this section, we'll cover some of the most important storage properties for Big Data applications.
Capacity
The amount of storage space needed is a big part of what the cost will be. As the amount of data increases, so does the need for more space to store it. It is important to look at your current storage needs and think about how they might change in the future. This will help you make sure that the storage option you choose can handle your data needs without costing you extra money.
For example, a large e-commerce company dealing with massive amounts of customer transaction data might require several petabytes of storage capacity to accommodate their data growth over time. To address these needs, the total volume of data and number of objects you can store in Amazon S3, fully managed serverless object storage service, are unlimited. Individual Amazon S3 objects can range in size from a minimum of 0 bytes to a maximum of 5 TB. See pricing details here.
Scalability
Scalability is the ability of a storage system to grow without any problems as the amount of data increases. If you choose a storage option that is scalable, you can add capacity as needed. This way, your storage costs will grow as your data does. Similarly, your costs will decrease if you get rid of some data. Scalable choices give you the freedom to scale up or down based on demand. This lets you get the best value for your money.
An example of scalability in storage would be the ability to seamlessly add more storage nodes or expand storage capacity without interrupting data access or compromising system performance. This allows organizations to scale their storage infrastructure as their data volume changes.
For instance, Azure Storage Accounts’s flexible and elastic infrastructure allows companies to grow or shrink to meet different needs and tasks. This lets companies store and get back huge amounts of data quickly. Azure also has a variety of storage services, such as Blob Storage, File Storage, Table Storage, and Queue Storage, each of which is meant to meet a different type of data storage need. By using features like auto-scaling, virtual network integration, and tiered storage options, Azure Storage Accounts make it possible for businesses to adapt their storage powers to changing needs in a way that is cost-effective, reliable, and gets the best performance.
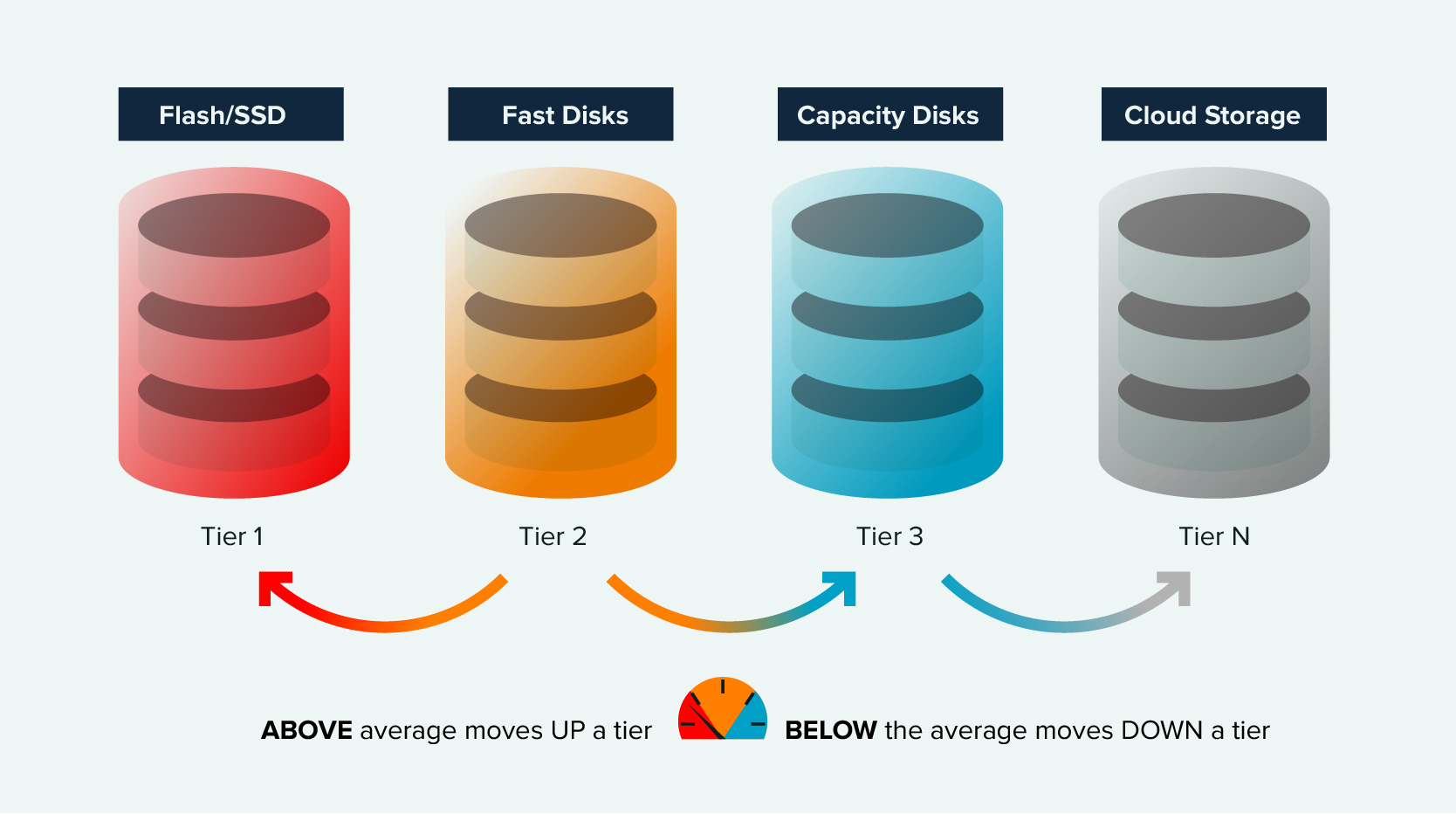
Tiers of Storage
With tiered storage, data is put into groups based on how often it is used and how well it needs to work. By using different storage options, you can make better use of your resources and cut costs. For instance, frequently accessed data may be stored on high-performance, solid-state drives (SSDs), while less frequently accessed data can reside on lower-cost, high-capacity hard disk drives (HDDs). This approach optimizes cost and performance by aligning storage resources with data access patterns.
For example, Splunk has different pricing tiers for workloads, ingest, entity, and activity-based requirements. You can see their pricing here. Another good option is Cloudera as their offerings are based on aspects like data engineering, data warehousing, machine learning, data hubs, and more. You can see their pricing plans here.
High Data Availability and Reliability
By thinking about how important and critical your data is, you can figure out how accessible it needs to be and allocate resources properly. High data availability ensures that data is accessible whenever needed, minimizing downtime and maintaining continuous operations.
For example, implementing data replication across geographically distributed data centers ensures redundancy and enables failover mechanisms to ensure uninterrupted access to critical data, even in the event of hardware failures or disasters.
For instance, Google Cloud Platform (GCP) offers strong and highly available options for storing data that make sure important information is always available. The high availability architecture of GCP is made so that it can handle breakdowns and always give users easy access to their data. With features like automatic data replication, redundant data, and distributed storage systems, GCP reduces the chance of losing data and makes sure that saved information is always available. Whether it's Cloud Storage for object storage, Cloud Spanner for globally consistent relational databases, or Cloud Bigtable for scalable NoSQL databases, GCP's data storage services are built to provide exceptional reliability and availability.
Data Security
It's important to think about your Big Data storage security needs and legal obligations before choosing a storage option that meets your security needs and saves you money. The cost of Big Data storage can go up if you use many strong security methods like encryption and access controls. On the other hand, weak security infrastructure may compromise sensitive or confidential data and damage a company's reputation. So there is a tradeoff between all tools you may use and what is reasonable based on data value. But some security services are mandatory for any enterprise-level Big Data storage: access control measures, such as role-based access control (RBAC), can ensure authorized access to data while preventing unauthorized access or data breaches, encryption data at rest and at transit, continuous monitoring and fraud detection.
Compliance Regulations
Some industries have specific rules about how long to keep data, how it can be checked, and who can view it. Features and abilities that are tied to compliance can affect the Big Data cost of storage. If you know what your regulatory requirements are, you can find storage options that meet those requirements without costing you more than necessary.
An example could be complying with data protection regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union. Ensuring that the chosen storage solution aligns with relevant compliance regulations helps organizations avoid penalties and maintain data integrity.
For instance, you can deploy cloud storage in a proper geographical region with security services for control purposes and to perform hybrid networking. Most leading cloud providers provide these types of services, integrations, and data centers in strategic locations to help address compliance regulations within those geographical and security aspects.
Costs of Big Data
Managing large amounts of data and making sure performance is at its best are important, but organizations must also think about how cost-effective a storage option for Big Data applications is. To get the best return on investment, you need to find a good balance between efficiency and cost. Storage options that can be scaled up or down, offer tiered storage, and have flexible pricing models let businesses match their Big Data cost for storage to their budgets. In the case of using cloud storage services, using tools that control budgeting and cost spending is mandatory.
Selecting the Right Option to Align With Your Big Data Storage
First, let's look at some of the most popular ways for organizations to store their data:
On-premises storage: This is the usual method, in which storage infrastructure is set up on the organization's own property. Storage area networks (SAN), network-attached storage (NAS), and direct-attached storage (DAS) are usually part of it. On-premises storage gives you direct control and actual access to your data, but it has Big Data cost implications up front and needs to be maintained regularly.
Cloud storage: Cloud storage has become very popular because it is easy to use, scalable, and offers several pricing options. Organizations can store and control their data using cloud service providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP). Cloud storage gives pay-as-you-go pricing, scalability on demand, and takes away the need to maintain infrastructure on-site.

Hybrid storage: As the name suggests, hybrid storage mixes the good things about both on-premises and cloud storage. It lets organizations keep important or sensitive data on-premises while using the cloud to store less important data in a scalable and cost-effective way; data can also be kept both on-premise and in the cloud as a backup option, or shared between on-premise and in the cloud based on regulatory requirements. Hybrid storage strikes a balance between control and flexibility, allowing businesses to tailor their storage systems to their needs.
Network-attached storage (NAS): NAS devices are directly linked to the network and store files. They are good for organizations that need to give different users and systems access to the same files and data. NAS is easy to manage, provides protection at the file level, and makes it easier to share data.
Storage area network, or SAN: A high-performance storage network that lets computers store data in blocks. They are often used in enterprise settings where applications need quick and direct access to storage resources. SANs can move data quickly, handle storage in a central location, and protect data in more advanced ways.
Object storage: Object storage is made to store big amounts of unstructured data, like documents, images, and videos. It saves data as objects and gives each object a unique identifier so that it is easy to find. Object storage is very scalable and gives high durability and data redundancy.
Planning Your Big Data Storage Cost
Carefully planning and budgeting for your storage needs, can help you ensure your resources are used in the best way possible while still meeting the needs of your business. Here are some ways to figure out how much your storage of Big Data costs will be.
- Assess the growth of your data. Start by looking at how much data you have now and estimating how much it will grow in the future based on past trends and business projections. Think about things like the rate of data creation, the rules for keeping data, and the expected sources of data. By knowing how your data grows, you can figure out how much space you'll need in the future.
- Analyze how data is accessed. Figure out how often and how important data access is for each statistic. Sort your data into groups based on how often it is accessed, such as hot, warm, or cold data. Hot data is data that is accessed often and needs a quick answer, while cold data is data that is accessed rarely. This analysis helps you figure out the right storage for Big Data tiers and where to put your resources.
- Think about scalability. Plan for scalability so you can handle more info in the future. Storage for Big Data solutions should have choices for scalability, so you can easily add more storage space as your data volume grows. This makes sure that you can meet the changing needs of your business without any downtime or expensive moves.
- Consider storage choices that won't break the bank. Look into different storage technologies and solutions that fit your budget and performance needs. Think about things like the cost of data quality, cost per terabyte, cost of data transfer, the ability to compress and remove duplicate data, and the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) over the lifespan of the storage. Cloud-based storage options, for example, often have pay-as-you-go pricing, which lets you scale your storage resources while minimizing costs of Big Data.
- Leverage data lifecycle management. Implement data lifecycle management techniques to optimize storage costs. Set up how long data will be kept and how it will be archived or deleted when it is no longer needed. By managing data well throughout its lifecycle, you can free up storage room and avoid spending money on things you don't need to.
- Plan for data protection and disaster recovery. Set aside some of your funds for storage for data protection tools, such as backups and solutions for dealing with disasters. It is important to protect your Big Data from hardware breakdowns, natural disasters, and cyber threats if you want to keep your business running and keep losses to a minimum.
- Review and improve storage use on a regular basis. Always keep an eye on how you use your storage and examine it to find inefficiencies or places where you can improve. Install storage monitoring tools that show you how your data is growing, how it is being used, and how it is being accessed. This knowledge can help you plan your storage space and decide how to use your resources in a smart way.
Remember that planning storage for Big Data is an ongoing process that needs to be looked at and changed often as your business changes and your data needs change. By being proactive and keeping an eye on your storage setting, you can make well-informed decisions to reduce your costs of Big Data storage and use the power of Big Data more effectively.
Big Data Storage: Getting it Right
Choosing the right option for enterprise data storage is important for organizations to manage their growing amounts of data and meet their storage and management needs. Businesses have a lot of storage options to choose from, like on-premises storage, cloud storage, hybrid storage, NAS, SAN, and object storage.
When choosing a storage option, it's important to find a good balance between control, ease of access, and cost-effectiveness. By carefully evaluating things like performance, scalability, security, cost, data governance, compliance, and availability, organizations can make choices that are in line with their business goals and objectives.
As an expert in the field of Big Data, Svitla Systems knows how hard and complicated it is to store enterprise data. We have the knowledge and experience to help organizations sort through the many storage choices and find the best one for them. Whether you need help designing a scalable cloud storage system, setting up a hybrid storage environment, or optimizing your on-premises storage infrastructure, we are here to help.
We can help businesses make the most of their data while keeping it safe, reliable, and easy to access. Contact us today to learn more about how our expertise in Big Data storage can help your company achieve seamless data storage, management, and valuable insights to fuel growth and innovation.





