Navigating personal finances can be tricky. Unexpected events like job loss, global crises, or even the temptation of a new trip can throw off financial goals. It's understandable why nearly 9 out of 10 people now use budgeting apps. These platforms aim to empower users to better understand and manage their money through technology.
Personal finance app development can be a good starting point if you're about to enter the fintech field. Intrigued? Let’s find out how to build one!
What is a Personal Finance App?
First, let’s briefly remind you what a finance app is. Simply put, it’s a mobile solution that helps people manage their money. Unlike banking apps connected to specific bank accounts, a personal finance management application provides a detailed review of how people control their funds. The goal is to make it simpler to control finances in one place.
Making personal finance apps is a good business for startups right now. More and more people have been using these apps over the last 4 years. In 2021, there were over 573 million downloads of money management apps in the US – a 19% increase from 2020.
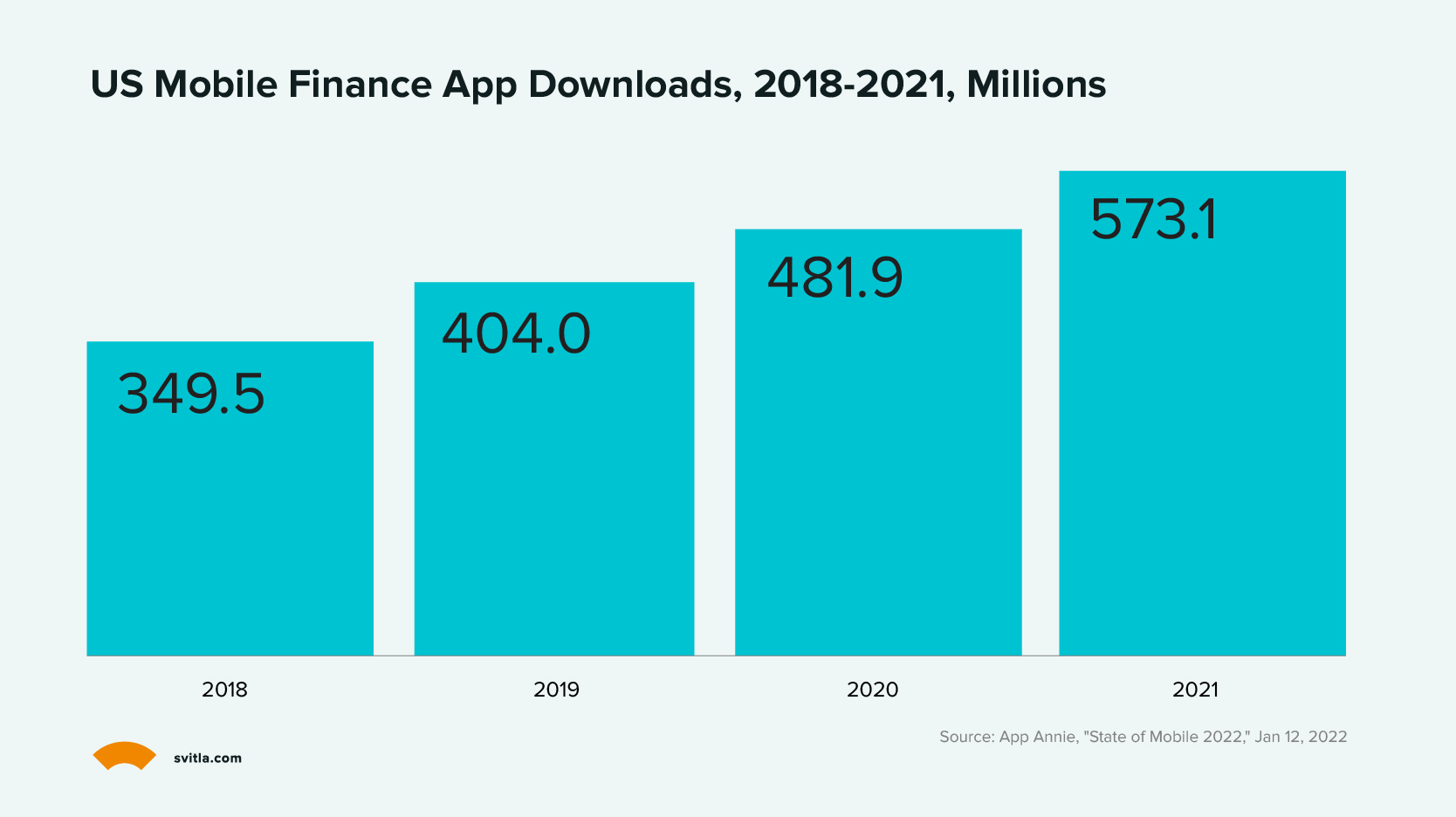
Finance apps also make up the largest share of all app types worldwide. This growth means there is a lot of potential for developers to succeed. But it also means there is a lot of competition.
To stand out, you need to understand what features help the top personal finance apps be so popular. Learning from the leaders can help your startup make a great app users want. But first, let’s explore the types of budgeting apps.
Types of Finance Apps
Budgeting apps offer a few options. Some apps keep things simple by focusing on one specific function, like tracking users’ spending. Others route and combine several budgeting features. There's no definitively “right” or “wrong” choice between a simple, specialized app and a complex, do-it-all app. Now, let’s explore the main types of finance apps.
Spending Trackers
Spending tracker apps connect to users’ bank accounts to automatically import and categorize their transactions. For example, they can separate how much users spend weekly on groceries, gas, shopping, bills, and other expenses. They provide visual graphs and charts that illustrate spending patterns over time. This allows users to analyze where their money is going and potentially identify areas to cut back. Tracking spending can make users more aware of daily purchasing decisions.
Budget Planners
Budget planner apps allow users to allocate specific amounts toward future expenses across different categories. For instance, if a user has $5,000 to organize an upcoming event, they would input that total amount and divide it amongst things like food, decor, entertainment, etc. The app makes sure users stay under their planned limits. Users can also use these apps for budgeting regular income, like a monthly paycheck. That way, they can plan to automatically save or invest a percentage instead of spending everything. Budget planners help create and stick to a plan that matches financial goals.
Investment Apps
Investment apps enable users to invest spare funds to grow their money over time instead of letting it sit idle. They provide a platform for buying and selling stocks, bonds, mutual funds, currencies, and other investments. Especially during COVID-19, many people have cut back on expenses for travel and shopping, freeing up extra cash to invest. These apps make it simple to get started investing and managing a portfolio. They offer education on intelligent investing strategies and tools to monitor market trends.
Top Personal Finance Apps Market Players
Now, that we’ve done with the main types of finance apps, let’s move and discuss the most prominent market players.
YNAB
You Need a Budget (YNAB) stands out for its user-friendly budgeting interface and helpful reporting encouraging paying off debt. YNAB was built around the proven zero-based budgeting methodology, where every dollar earned is proactively allocated towards financial goals like living expenses, discretionary spending, or growing savings.
This goal-driven approach keeps users focused on constructive priorities rather than restricting spending. YNAB's flexible categorization allows budgets to be tailored to a user’s unique circumstances.
Cost: 34-day free trial, then $99/year or $14.99/month
Device: Android / iPhone
Review score: Google Play: 4.2/5, Apple Store: 4.8/5
Spendee
Spendee accommodates the growing need for transparent, collaborative financial management through features like shared wallets and group transaction oversight. The app automatically syncs connected bank account activity from all household members. Users can seamlessly split or combine expenses, transfer funds between wallets, and maintain common budgets for goals like vacations, bills, and more.
Cost: Free for the basic version, $14.99/year for Spendee Plus, or $22.99 for Spendee Premium
Device: Android / iPhone
Review score: Google Play: 4.2/5, Apple Store: 4.6/5
CountAbout
CountAbout delivers extensive personalization options targeting detail-oriented budgeters. Users can create highly customized categories, income sources, graphical reports, and transaction splits. Recurring transfers between user-defined accounts are simple to configure. While CountAbout focuses more on manual transaction entry over automation, its flexible architecture supports intricate financial plans.
Cost: 45-day free trial, then $9.99/year for a standard plan or $39.99/year for a premium plan
Device: Android / iPhone
Review score: Google Play: 4.6/5, Apple Store: 4.4/5
Mint
As one of the earliest and most trusted personal finance apps, Mint emphasizes safe, automated expense tracking and basic budgeting. By securely connecting over 16,000 financial institutions, Mint automatically imports recent user transactions using bank-level encryption protocols. It intelligently categorizes spending history to provide hands-off monitoring. With multi-year trends and typical expenditures for common purchase categories, Mint allows users to spot irregular spending easily.
Cost: Free or $4.99/month
Device: Android / iPhone
Review score: Google Play: 4.0/5, Apple Store: 4.8/5
Key Features of Personal Finance App
In this section, we’ll explore the main functionality each solid personal finance application must have.
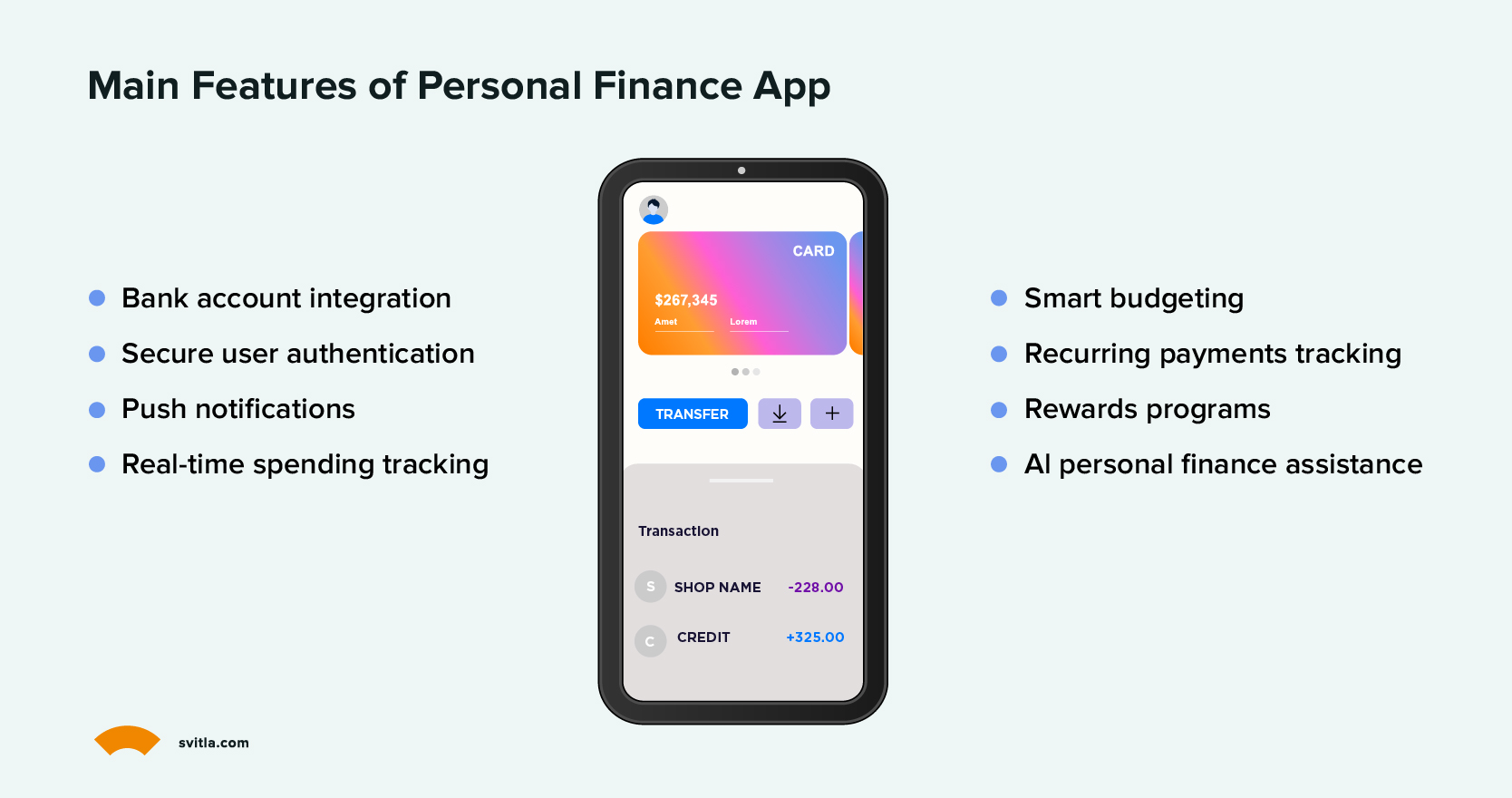
Bank Account Integration
This feature allows users to connect all their financial accounts, like bank accounts, credit cards, or investment accounts, to an app. Hence, they have a unified dashboard to view real-time balances and transactions from all linked accounts. In this way, users enjoy easier money management, consolidated insights into overall financial health, spending patterns analysis, and eliminating manual tracking across accounts.
Secure User Authentication
User identity verification is critical for finance apps to prevent fraud or unauthorized access. Methods like biometric authentication (fingerprint, face ID) and two-factor authentication (one-time passwords sent via SMS or email) provide enhanced security. Such multi-layered authorization makes it extremely difficult for hackers to gain entry and protect sensitive user data.
Push Notifications
Timely alerts about financial activities allow users to stay updated and address issues quickly. Notifications for salary deposits, significant transactions, bill-due alerts, account balance thresholds, and suspicious login attempts to allow users to manage money proactively. Personalized messages can also provide positive reinforcement when savings goals are met.
Real-Time Spending Tracking
Instant updating of transactions from linked accounts provides dynamic insights compared to periodic statements. Up-to-the-minute tracking allows quick corrections to overspend and reinforces discipline. Spending patterns analysis can also inform smarter budgeting decisions.
Smart Budgeting Features
Advanced analytics to process income, expenses, and transaction data and provide personalized tips and recommendations that promote better saving and spending habits. Analytics can also highlight budget problem areas, give money-saving advice based on behavior patterns, and track progress over time.
Recurring Payments Tracking
It enables creating payment profiles for regular expenses like EMIs, utility bills, or subscriptions. The app reminds due dates, facilitates auto-payments, and tracks statuses. Ensures timely payments and prevents late fees.
Rewards Programs
Rewards programs are a great way to incentivize users. They can come in different shapes or forms. One of the common ways is to introduce points earned for responsible money management behaviors that can be redeemed for gift cards, shopping/dining discounts, or statement credits. Creates positive reinforcement that makes finance apps “sticky” via gamification. It also fosters habits like saving and debt repayment.
Al Personal Finance Assistance
AI helps users to analyze their income, expenses, debts, and financial goals to provide tailored money management recommendations. Unlike simple expense trackers, this intelligent assistant gets to know users’ financial situation individually to offer insightful advice and actionable ways to optimize spending, saving, investing, and reaching financial targets. With ongoing use, AI continues refining its guidance to empower smarter financial planning and decision-making.
How to Build A Personal Finance App Step-by-Step
Now that you’re familiar with the basics, let’s explore how to create a personal finance app in 9 steps with the MVP approach.
Step #1. Conduct Market Research
Explore existing personal finance apps available on the market. It helps you to understand users’ expectations and needs. Conduct interviews or feasibility studies to identify target market pain points and tailor app features accordingly.
Step #2. Define Your App's Features and Purpose
Consider the main features that would make your app useful – visualization, payment reminders, budget tracking, and goal setting. Consider successful apps like Mint and Albert for inspiration. Mint, for example, focuses on visualization to present finances in an easily understandable way.
Step #3. Plan Necessary Integrations
Look into APIs like Plaid and Stripe that let your app seamlessly connect to bank accounts, payment systems, and other finance apps. Those integrations smooth out the user experience.
Step #4. Prioritize Security Measures
Financial apps hold sensitive data, so security is crucial. Encryption, biometrics, two-factor sign-ins – build all that in. Carefully protect data in transit, too. Make sure your app follows standards like GLBA, GDPR, PCI DSS.
Step #5. Choose the Right Tech Stack
Once you've outlined your personal finance app's features, integrations, and security measures, the next step is determining the tools required to turn these concepts into reality. Your initial decision involves selecting the programming language best suited for your project.
Svitla System will help you choose the best technology stack for fintech products to accelerate development and create a product that is easy to maintain.
Step #6. Design an Intuitive, User-Friendly App
A personal finance app must be simple, secure, and reliable for users handling financial tasks. Fundamental principles include allowing users to do multiple tasks in one app, keeping actions straightforward, and using clear language. It’s also essential to add visual elements like graphs and charts, so users can quickly overview their financial situation and related trends.
Step #7. Build an MVP
Focus on core features for the MVP, such as budget tracking and visualization, to attract users and investors. Conduct market research and testing during the MVP development to validate the app's real-world viability.
Step #8. Launch the App
Launching an app doesn’t end with the actual launch and publishing it on app stores.
Keep users interested by regularly offering them valuable content and timely updates based on their feedback and market demand.
Common Personal Finance App Development Challenges
Banking app development is associated with some risks. Let’s discuss what issues you can meet and how to handle them.
Security Concerns
Data security is critical when creating financial apps, especially for mobile devices. Statistics show many weaknesses – over 80% of Android devices and 25% of Google Play apps have flaws. As developers, ensuring data stays private and securing against risks should be our main concern.
Users give applications sensitive financial details and expect that data to stay safe. One leak of credit card info could permanently damage an app's trustworthiness. By teaming up with data and security experts early on, you can protect against cybercriminals ahead of time. Building strong privacy protections before release is essential.
Solution: Take several steps to address security risks. First, conduct ongoing risk checks to find vulnerabilities. Multifactor authentication to confirm user identities is a must feature in fintech applications. Encrypt sensitive personal data end-to-end. Also, perform regular internal and external security reviews and penetration testing. This helps spot weaknesses early.
Data Regulatory Compliance
The financial industry has many regulations. Studies show over 50% of financial apps initially fail to meet all those rules. Ensure your app follows regulations and standards like PCI DSS, GDPR, and AML.
Keeping user trust and safety first means making compliance a priority. Doing this gives financial apps the best chance of succeeding as laws rapidly change. Having an ethical base and resources to update requirements lets innovation continue. These apps working long-term depend on regularly accessing the latest rules.
Solution: Consider hiring dedicated staff that thoroughly monitors financial rules, update apps on new regulations, and check that apps follow requirements. You should also build regular checks through the design process to catch problems. Before launch, you should confirm apps meet standards. Look into advanced tools to track new laws and automate compliance parts. Maintain a searchable database that makes it easy for developers to stay up-to-date on regulations and raise transparency to keep everyone posted on new updates.
Retention Challenge
Mobile app retention is a widespread challenge, especially for finance apps. Users often download apps just to browse, then delete them if the experience proves underwhelming – too complex, dull aesthetics, inconvenient access, and organization. Yet, finance apps aim to simplify inherently complicated processes. Without thoughtful design, they achieve the opposite, driving users away.
Solution: To promote client retention, finance apps should focus on meaningful engagement like customized messages and in-app assistance to demonstrate value. The more apps showcase how they simplify users' lives, the more indispensable they become. Additionally, timely push notifications keep users informed without risking irritation. By providing a personalized, convenient, and responsive experience, finance apps can shift from a temporary curiosity to an essential daily tool.
How to Make Money on a Personal Finance App
You have finally developed a money management app after lots of hard work. Now you need to make money from the app. Here are some excellent ways to do that:
In-App Purchases
Offer a free app with limited features. Sell premium features like advanced budgeting tools, debt payoff trackers, investing dashboards, and money forecasts as in-app purchases. Price these upgrades based on the value they provide.
Advertisement
Display banner or interstitial ads at natural breaks in the app flow. Research shows financial apps can earn $5-$15 per thousand ad impressions. Be careful not to overdo it, or the app experience will suffer.
Subscriptions
Charge a monthly fee for access to premium features like custom budget templates, unlimited transactions, financial advisor access, and customized money tips. Offer discounts for annual subscriptions.
Affiliate Marketing
Add links or offers for financial products like credit cards, bank accounts, insurance, and loans that pay you an affiliate commission. Only promote relevant offers that benefit users.
Data Monetization
Analyze anonymized and aggregated user data to develop spending insights. Sell these reports to financial institutions to help them improve products. Or use insights to build personalized money tools.
Additional options could include one-time consulting fees, selling promotional space to relevant brands, or peer-to-peer transaction fees if enabling payments.
To Conclude
Creating a personal finance app has lots of potential. With more people looking to get a better handle on their money, having an easy-to-use spending tracker or investment tool in their pocket makes a lot of sense.
Regarding types, you have to decide if you want your app to be more of a spending tracker, budget planner, or investment helper. Maybe it could even try to cover all of this functionality. It should include linking bank accounts to auto-import transactions and tracking where the money's going.
Keeping personal data safe has to be priority number one. Encryption protocols and fingerprint login instead of passwords are the must-haves of your future app. Don't cut corners there. Managing money is no fun, but your app can help people do it better.
Have an idea for a personal finance management app development in mind? Svitla Systems is here to help you. Do contact us so we can discuss and estimate your future project.





